- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- How to Trade with Momentum Trading
- How Does Momentum Trading Work?
- Elements of Momentum Trading
- Momentum Trading Strategies
- Momentum Trade Setup
- Momentum Indicators
- Advantages of Momentum Trading
- Disadvantages of Momentum Trading
- Common Mistakes in Momentum Trading
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Momentum Trading?
- How to Trade with Momentum Trading
- How Does Momentum Trading Work?
- Elements of Momentum Trading
- Momentum Trading Strategies
- Momentum Trade Setup
- Momentum Indicators
- Advantages of Momentum Trading
- Disadvantages of Momentum Trading
- Common Mistakes in Momentum Trading
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Momentum Trading?
What is Momentum Trading? Meaning, Strategies & Benefits
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Oct 29, 2025 08:19 PM IST
Momentum trading is a strategy where you buy assets that are going up in price and sell ones that are going down, based on the idea that price trends usually continue for some time. In momentum trading traders aim to capitalise on market volatility by identifying stocks or instruments showing strong price movement and entering positions early in the trend.
What is Momentum Trading?
Momentum trading meaning refers to a strategy where traders buy securities that are rising in price and sell them when they show signs of peaking. It is based on the idea that assets showing strong price movement will continue to move in the same direction for a certain period. Traders use tools like volume analysis, RSI, and moving averages to identify trends and make quick entry and exit decisions.
Example:
Assume a stock has been rising continuously due to strong earnings results. A momentum trader identifies the upward trend using technical indicators and enters a buy position. As long as the stock maintains its upward momentum, the trader holds the position and exits when the indicators show a slowdown or reversal in trend.
This strategy works best in volatile markets, requires quick decision making and strong risk management.
How to Trade with Momentum Trading
Momentum trading involves identifying stocks with strong price trends and acting quickly to capitalise on short-term gains. Timing and discipline are key.
- Breakout Trading: Enter a trade when the price breaks above resistance or below support with strong volume, signaling a new trend.
- Trend Following: Ride the momentum by entering during pullbacks within an existing trend, using moving averages or trendlines for confirmation.
- Volume-Based Confirmation: Combine price action with high trading volumes to confirm strong momentum before entering a trade.
- Indicator-Based Entry: Use technical tools like RSI, MACD, or Momentum Indicator to identify overbought/oversold conditions or momentum shifts.
- News-Based Momentum: Trade based on strong market-moving news (e.g., earnings, mergers), which can trigger rapid price movements.
- Sector Rotation: Identify sectors gaining strength and trade the top-performing stocks within those sectors for short-term momentum plays.
How Does Momentum Trading Work?
Momentum trading works in a simple way, Stocks or assets that are moving in one direction with strength are likely to continue moving in that direction for a while. Traders using this method look for signs that a stock has gained “momentum” and try to ride that wave for as long as possible.
- Spot the Trend: Traders identify a stock or asset that is gaining speed either moving sharply upward or downward.
- Use Technical Indicators: Tools like RSI, MACD, or moving averages help confirm the strength of the trend.
- Volume Check: High trading volume usually supports strong momentum. It shows more market participants are involved.
- Enter the Trade: Once the trend and momentum are confirmed, the trader enters a position in the direction of the move.
- Stay Alert: Momentum doesn’t last forever. Traders closely watch for signs of slowing or reversal.
- Exit Smartly: When the indicators or price action suggest momentum is fading, traders exit to lock in profits or prevent losses.
Elements of Momentum Trading
These elements work together to help traders capture short-term moves and maximise potential gains while managing risk.
- Price Action: Momentum trading relies heavily on observing price trends. A sharp upward or downward movement indicates potential entry opportunities.
- Volume: High trading volume supports the strength of a trend. Strong momentum is often confirmed when volume increases alongside price movement.
- Technical Indicators: Tools like RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD, Moving Averages, and Momentum Indicator help identify entry and exit points.
- Trend Direction: Traders focus on identifying whether the market is in an uptrend or downtrend and trade in the direction of the prevailing momentum.
- Entry and Exit Signals: Breakouts, pullbacks, or indicator signals serve as cues to enter or exit trades. Timing is critical in momentum trading.
- Volatility: Momentum strategies perform better in volatile markets where price movements are stronger and quicker.
- Risk Management: Setting stop-loss and target levels is essential to protect against sudden reversals and to manage position size effectively.
Momentum Trading Strategies
Each strategy requires disciplined execution, strong risk management and confirmation through technical tools.
- Breakout Strategy: Enter a trade when the price breaks above resistance or below support with strong volume, indicating a new trend.
- Moving Average Crossover: Use short-term and long-term moving averages. A bullish crossover (short-term MA crossing above long-term MA) signals buy; bearish crossover signals sell.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) Strategy: Identify overbought (above 70) or oversold (below 30) conditions. Strong momentum near these levels may indicate trend continuation or reversal.
- MACD Momentum Strategy: Use the MACD line crossing above the signal line to spot bullish momentum and vice versa for bearish signals.
- Volume-Weighted Strategy: Combine price movements with rising volume to confirm strong momentum. High volume with price surge signals strong interest.
- Pullback and Continuation: Wait for a temporary pullback in a strong trend, then enter the trade once momentum resumes.
- Gap Trading Strategy: Trade stocks that open significantly higher or lower than the previous day’s close, often driven by news or earnings.
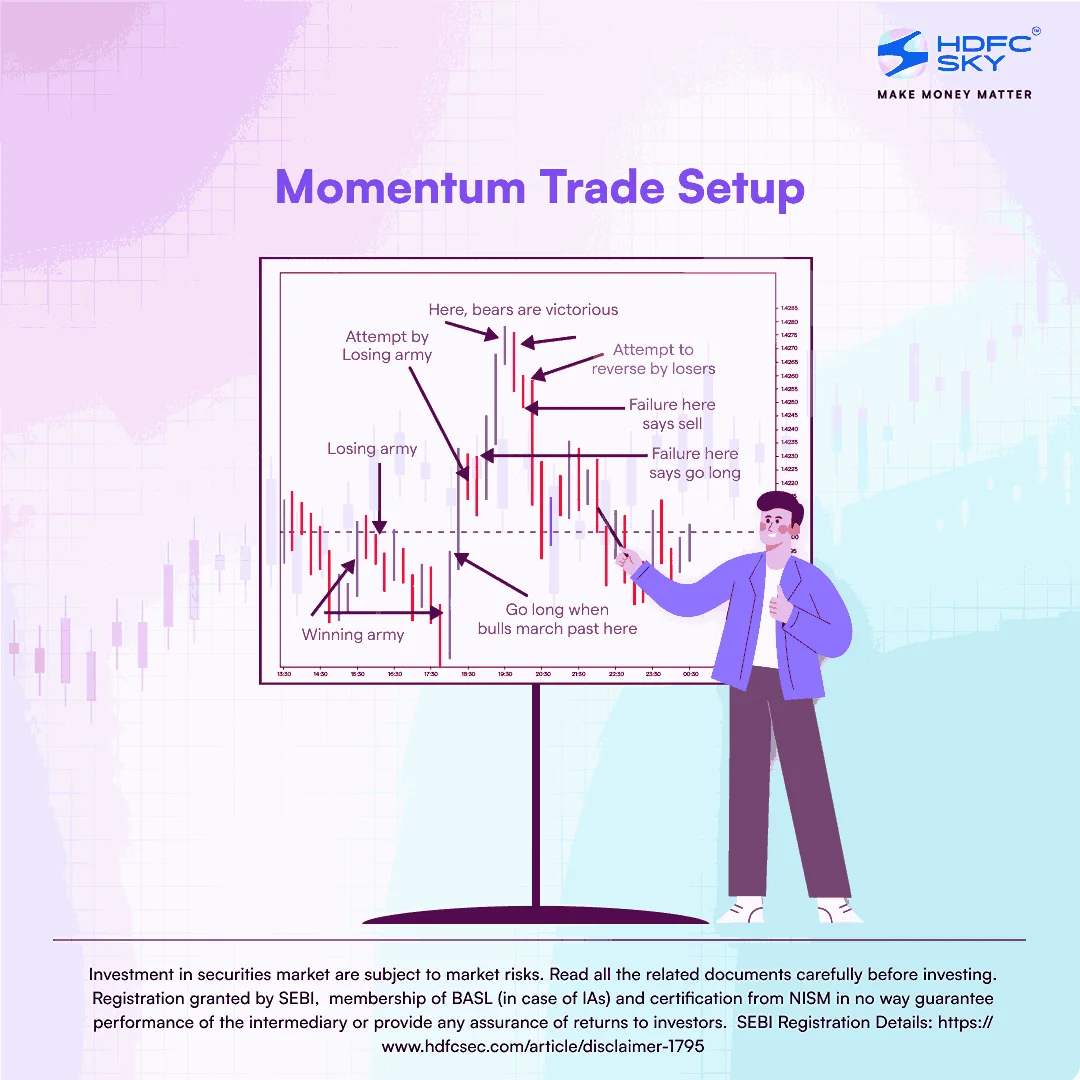
Momentum Trade Setup
Momentum Indicators
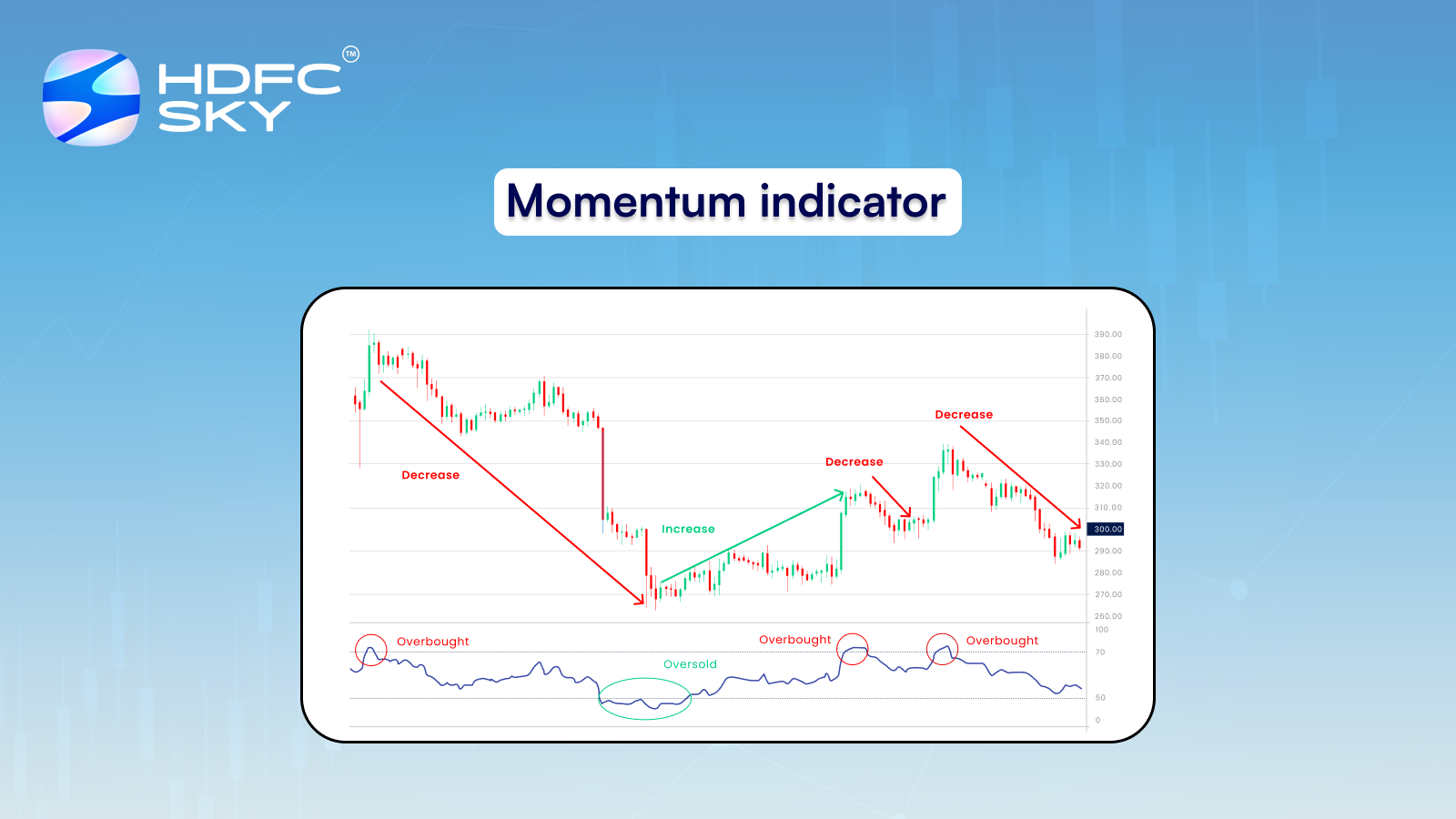
In the technical analysis series, we have discussed several momentum indicators. These include RSI (8.5), MACD (8.7), Stochastic Oscillator (8.8) and ROC (8.10).
Rules
Here are four rules that will improve your chances of being successful in momentum trading strategy:
- Stocks selected should have enough liquidity. This will ensure that you are able to enter and exit at desired prices.
- Timing is key. Only enter a trader when the momentum is accelerating and exit when the momentum is losing pace.
- Use rupee cost averaging, i.e., buy at multiple prices and sell at multiple prices, to further lower your risk.
- Beware of external factors. These include economic, demographics, legal, political, technological and natural forces. Markets react poorly to shocks. Any negative news could reverse the uptrend in a stock.
Advantages of Momentum Trading
Momentum trading focuses on capitalising on strong price trends for short-term gains. It can be highly rewarding when market conditions are favourable and trends are clear.
- Quick Profits: Traders can capitalise on strong short-term price movements in either direction.
- Works Well in Trending Markets: In a strong bullish or bearish trend, momentum strategies can produce consistent gains.
- High Liquidity: Popular momentum stocks or assets usually have high trading volumes, making it easier to enter and exit trades quickly.
- Leverage with Technical Indicators: Tools like RSI, MACD and Moving Averages can help identify entry and exit points effectively.
- Can Outperform in Volatile Phases: Momentum strategies often capture the most profitable part of a strong market move.
Disadvantages of Momentum Trading
While momentum trading offers profit potential, it also carries significant risks. Sudden market reversals or false signals can quickly turn gains into losses.
- High Risk of Losses in Sideways Markets: Momentum trading fails when the market is choppy or lacks clear direction.
- Requires Constant Monitoring: Traders need to track positions closely as trends can reverse quickly.
- False Signals: Technical indicators may give wrong buy/sell signals during volatile or unpredictable conditions.
- Emotional Pressure: Rapid price changes can trigger fear or greed, leading to poor decisions.
- Higher Transaction Costs: Frequent buying and selling can lead to significant brokerage and tax costs.
Common Mistakes in Momentum Trading
Momentum trading can be profitable but also risky if common pitfalls aren’t avoided. Many traders make mistakes that impact their returns and increase losses.
- Ignoring market trends and trading against momentum
- Overtrading without proper analysis
- Poor risk management and lack of stop-loss orders
- Chasing stocks after the momentum has faded
- Not having a clear exit strategy
- Letting emotions drive trading decisions
- Failing to adapt to changing market conditions
Avoiding these errors can improve your chances of success in momentum trading.
Conclusion
Momentum trading strategy uses the pace of price changes to take advantage of ongoing market trends. By entering positions once trends are confirmed and exiting as momentum slows, traders can potentially achieve higher profits while minimising risks. However, it requires a good understanding of technical analysis and can be time consuming.
Related Articles
FAQs on What is Momentum Trading?
Is momentum trading profitable?
Yes, it can be when strong trends exist, but it requires skill, discipline, and proper risk management.
What are the risks of momentum trading?
Market reversals, false breakouts, and high emotional pressure can lead to losses.
What are the advantages of momentum trading?
Lower risk due to confirmed trends, higher profits by riding price bursts, and benefiting from market volatility.
What are the disadvantages of momentum trading?
Ineffective in consolidating stocks, higher brokerage costs, requires deep technical analysis knowledge, and can be time-consuming.



