- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is Scalping Trading?
- How Does Scalping Trading Work?
- How Do Scalpers Analyse the Market Before Scalping?
- How to Choose Stocks for Scalping
- When selecting stocks for scalping, also consider the following
- Scalping Trading Strategy
- Advantages of Scalping Trading
- Disadvantages of Scalping Trading
- What are the Risks and Challenges of Scalp Trading?
- Difference Between Scalping as a Primary Style and Supplementary Style
- Scalping vs Swing Trading
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Scalping in Trading
- What is Scalping Trading?
- How Does Scalping Trading Work?
- How Do Scalpers Analyse the Market Before Scalping?
- How to Choose Stocks for Scalping
- When selecting stocks for scalping, also consider the following
- Scalping Trading Strategy
- Advantages of Scalping Trading
- Disadvantages of Scalping Trading
- What are the Risks and Challenges of Scalp Trading?
- Difference Between Scalping as a Primary Style and Supplementary Style
- Scalping vs Swing Trading
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Scalping in Trading
What is Scalping Trading? Meaning, Risks and Challenges of Scalp Trading
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Oct 23, 2025 05:26 PM IST
Scalping trading is a short-term trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from minor price movements in the market. Trades are held for just a few seconds to minutes relying on high trading volume and quick decision-making. This strategy requires focus, discipline and fast execution, as gains from each trade are small but can accumulate over multiple trades throughout the day.
What is Scalping Trading?
Scalping trading meaning refers to a short-term trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from very quick trades, often held for seconds or minutes. Scalpers capitalise on minor price fluctuations in highly liquid markets, executing multiple trades in a day. This approach requires quick decision-making, strict risk management and constant market monitoring to accumulate profits over numerous small trades.
How Does Scalping Trading Work?
How to do scalping trading involves making quick, small-profit trades while managing risk effectively. Thus understanding how does scalping trading works requires looking at the mechanics of short-term trading.
- Identifying Trade Setups: Traders use technical tools like moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index) and Bollinger Bands to determine entry and exit points.
- Placing Quick Trades: Scalpers may execute multiple trades within minutes to capture minor price fluctuations.
- Managing Risk: Using stop-loss orders ensures that one big loss does not wipe out multiple small gains.
- Taking Advantage of Liquidity: Scalping works best in liquid markets where price movements are frequent and trade execution is instant.
Let’s look at a scalping trading example: A scalper might buy 1000 shares of a stock at ₹500 when technical indicators suggest a small upward movement is likely. If the price rises to ₹500.50, the scalper might sell immediately, making a ₹500 profit before commissions. This process might be repeated multiple times throughout the trading day.
The success of scalping trading strategy depends heavily on the following:
- A reliable and fast trading platform
- Low transaction costs
- The discipline to take small profits and cut losses quickly
- The ability to make rapid decisions under pressure
- A deep understanding of market microstructure and price action
How Do Scalpers Analyse the Market Before Scalping?
Scalpers use a combination of technical analysis, market indicators and real-time data to make quick trading decisions:
- Technical Charts: They study short-term charts, such as 1-minute or 5-minute candlestick charts, to identify trends, support and resistance levels.
- Volume Analysis: High trading volume often signals strong price movements, which scalpers use to time their entries and exits.
- Price Action: Scalpers closely observe price patterns, candlestick formations and recent market behaviour to predict immediate price movements.
- Technical Indicators: Tools like moving averages, Bollinger Bands and Relative Strength Index (RSI) help scalpers confirm trends and overbought or oversold conditions.
- Market Depth and Order Book: By monitoring buy and sell orders, scalpers gauge market sentiment and potential short-term price swings.
Through these methods, scalpers aim to quickly identify opportunities for small, profitable trades while minimising risk.
How to Choose Stocks for Scalping
Selecting the right stocks is crucial for successful scalping. Traders typically look for:
- High Liquidity: Stocks with high trading volumes allow quick entry and exit without significant price slippage.
- Low Spread: Stocks with a small difference between the bid and ask price help scalpers maximise profits on small price movements.
- Volatility: Moderate to high volatility is preferred, as scalpers rely on frequent price fluctuations to make quick gains.
- Market News and Events: Stocks affected by recent news, earnings reports or announcements can offer short-term trading opportunities.
- Consistent Patterns: Stocks that follow predictable intraday trends are easier for scalpers to analyse and trade efficiently.
By focusing on these factors, scalpers increase their chances of executing quick, profitable trades while managing risk.
When selecting stocks for scalping, also consider the following
When selecting stocks for scalping, also consider trading hours, sector performance, price range and recent volume spikes. These factors help identify stocks with strong short-term movement potential.
- Trading Hours: Some stocks are more active during certain times of the day, especially at market open and close.
- Sector Performance: Stocks in strong-performing sectors may offer more predictable short-term movements.
- Price Range: Stocks with a reasonable price range are easier to scalp, as very low or very high-priced stocks can be riskier.
- Recent Volume Spikes: Stocks experiencing sudden increases in volume can indicate potential short-term opportunities.
- Historical Intraday Volatility: Analysing how a stock moves within a day can help predict short-term price swings for scalping.
Considering these factors helps scalpers identify stocks with the best potential for quick, profitable trades.
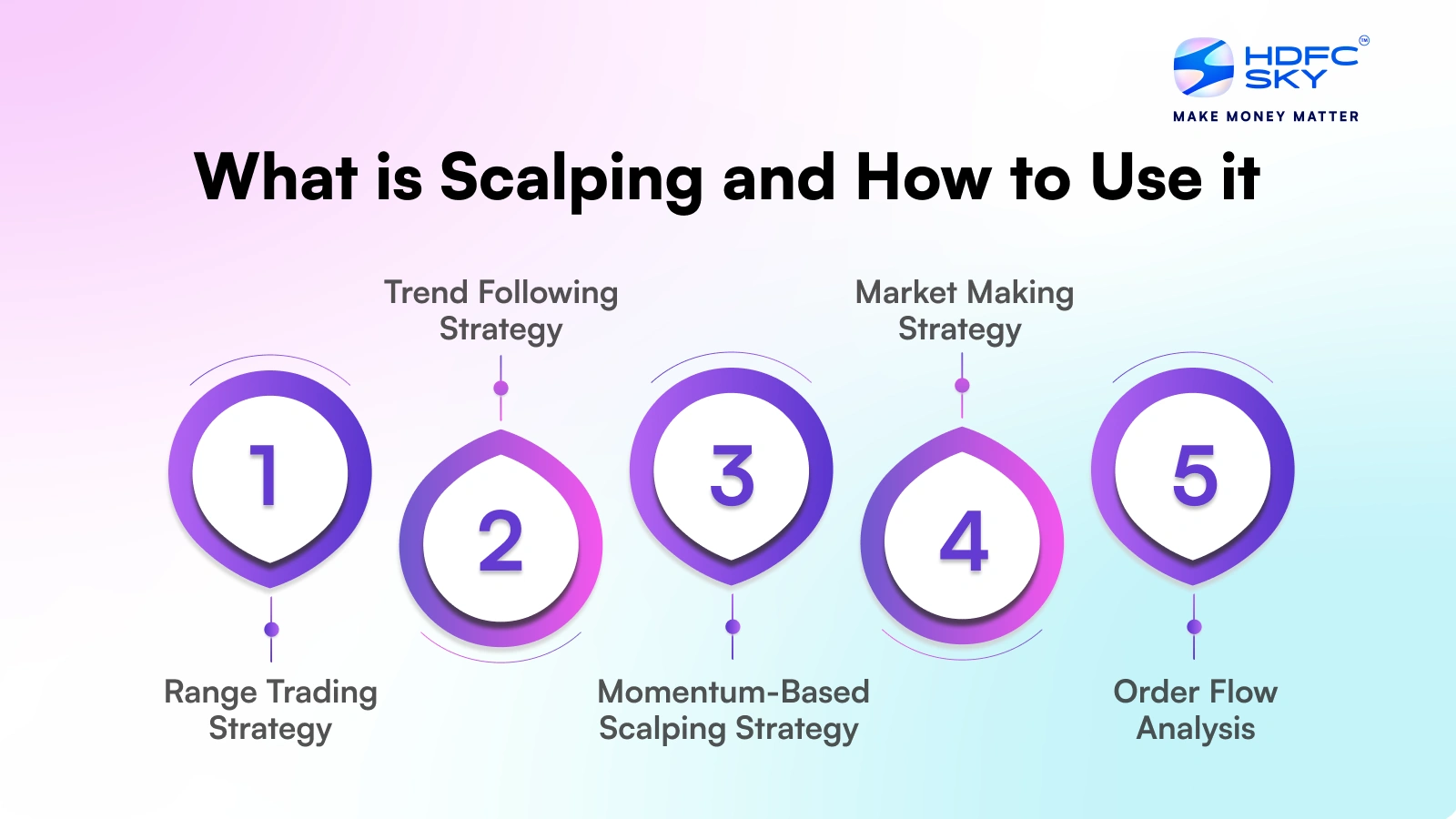
Scalping Trading Strategy
There are several effective scalping trading strategies for beginners that traders use to capture quick profits:
1. Range Trading Strategy
The Range Trading Strategy involves identifying support and resistance levels and trading the bounces between these levels. Scalpers buy near support and sell near resistance, capturing small moves within the established range. This strategy works best in sideways or consolidating markets where price oscillates within defined boundaries.
2. Trend Following Strategy
The Trend Following Strategy focuses on capturing small portions of a stronger trend. Scalpers wait for pullbacks or consolidations within an established trend and enter the direction of the primary trend. This approach follows the principle of “the trend is your friend” but on a much shorter timeframe than traditional trend following.
3. Market Making Strategy
The Market-Making Strategy attempts to profit from the bid-ask spread by placing limit orders on both market sides. This strategy is one of the most challenging for individual traders, as it has traditionally been the domain of market makers and high-frequency trading firms. To execute effectively, it requires sophisticated algorithms and extremely low latency.
4. Momentum-Based Scalping Strategy
Momentum-based scalping involves identifying and trading stocks showing strong short-term momentum. Scalpers look for sudden volume and price movement increases, often triggered by news events or breakouts from technical patterns. They enter positions in the direction of the momentum and exit quickly before the momentum fades.
5. Order Flow Analysis
Order Flow Analysis is a more advanced strategy in which scalpers analyse the flow of buy and sell orders to predict short-term price movements. This strategy requires access to Level II market data and a deep understanding of how institutional orders affect market dynamics.
Scalpers also use a variety of technical indicators to guide their strategies, including:
- Moving averages (notably 5, 9 or 20-period)
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
- RSI (Relative Strength Index)
- Bollinger Bands
- Volume indicators
- Tick charts or time-based charts with short intervals (1 minute or less)
Successful scalpers typically develop their own hybrid strategies that combine elements from different approaches and adapt them to their personal trading style, risk tolerance and the specific characteristics of the markets they trade.
Advantages of Scalping Trading
Scalping trading allows traders to earn quick profits by capitalising on small price movements. It also reduces exposure to overnight market risks.
- Quick Profits: Scalping allows traders to make small profits repeatedly within a short time, which can add up over the day.
- Lower Market Exposure: Since trades are held for very short periods, scalpers are less affected by overnight market risks or sudden news events.
- High Trading Opportunities: Frequent price movements provide multiple opportunities to enter and exit trades in a single session.
- Discipline and Skill Development: Scalping requires quick decision-making and strict risk management, helping traders sharpen their market skills.
- Capital Efficiency: Traders can leverage smaller price movements to generate returns without needing large capital for long-term positions.
Disadvantages of Scalping Trading
Scalping trading can be stressful and requires constant market monitoring. Frequent trades also lead to higher transaction costs, reducing overall profits.
- High Stress Levels: Scalping requires constant focus and quick decision-making, which can be mentally exhausting.
- Increased Transaction Costs: Frequent trading leads to higher brokerage fees and commissions, which can reduce overall profits.
- Requires Advanced Skills: Success in scalping demands strong technical analysis skills and experience in reading market patterns.
- Limited Profit per Trade: Each trade offers only a small profit, so losses from a few trades can quickly offset gains.
- Time-Consuming: Even though trades are short-term, scalpers must monitor the market continuously during trading hours.
What are the Risks and Challenges of Scalp Trading?
These risks make scalping a challenging strategy, requiring discipline, experience and careful risk management.
- Market Volatility: Sudden price swings can lead to unexpected losses, as scalping relies on small, precise movements.
- High Transaction Costs: Frequent buying and selling incur significant brokerage fees and commissions, which can eat into profits.
- Execution Risk: Delays in order execution or slippage can impact the profitability of rapid trades.
- Emotional Stress: The fast-paced nature of scalping can cause stress, leading to impulsive decisions and mistakes.
- Limited Time for Analysis: Scalpers must make decisions in seconds, leaving little room for thorough research or consideration.
- Dependency on Technology: Successful scalping requires reliable trading platforms, fast internet and real-time data; technical failures can result in losses.
Difference Between Scalping as a Primary Style and Supplementary Style
| Feature | Scalping as a Primary Style | Scalping as a Supplementary Style |
| Purpose | Used as the main trading strategy to generate profits | Used alongside other strategies like swing or position trading to enhance overall returns |
| Focus | Entire trading approach revolves around short-term, quick trades | Only a portion of trades are scalped while other trades follow longer-term strategies |
| Time Commitment | Requires constant market monitoring throughout the trading session | Requires monitoring only for specific trades or market conditions |
| Profit Goal | Small, frequent profits accumulated over the day | Complements profits from other trading strategies; not the primary income source |
| Risk Exposure | High due to rapid decision-making and frequent trades | Moderate, as scalping is applied selectively |
| Trader Type | Highly active traders who can handle stress and fast-paced environments | Traders who prefer a balanced approach combining short-term and longer-term trades |
Scalping vs Swing Trading
| Feature | Scalping Trading | Swing Trading |
| Time Frame | Very short-term, from seconds to minutes | Short to medium-term, from a few days to weeks |
| Number of Trades | High frequency, multiple trades per day | Fewer trades, focusing on capturing larger price moves |
| Profit per Trade | Small profits per trade | Larger profits per trade |
| Market Exposure | Low, minimal overnight risk | Higher, positions held overnight or longer |
| Analysis Method | Focuses on technical analysis, charts and intraday price action | Uses a combination of technical and fundamental analysis |
| Stress Level | High, requires constant monitoring | Moderate, less intense than scalping |
| Transaction Costs | Higher due to frequent trades | Lower as trades are less frequent |
| Ideal For | Traders seeking quick, small gains | Traders aiming for bigger gains over a longer period |
Conclusion
Scalping trading offers a unique approach to the markets that can reap potential returns for traders with the right temperament, skills and resources. By focusing on capturing multiple small price movements throughout the trading day, scalpers can potentially generate consistent profits while limiting their exposure to broader market risks. The success of a scalping trading strategy depends on several critical factors: disciplined execution, appropriate stock selection, effective risk management and the ability to make quick decisions under pressure. The best scalpers combine technical analysis with an intuitive feel for market dynamics developed through experience. For those interested in exploring how to do scalping trading, start with paper trading or very small position sizes while developing your strategy. As with any trading approach, education, practice and continuous refinement are key to long-term success
Related Articles
FAQs on Scalping in Trading
How much capital is needed for scalping?
Scalping requires sufficient capital to cover frequent trades and transaction costs. The minimum capital for scalping may vary from trader to trader, but since scalping involves intraday trades, your broker will provide you with extra margin benefits as per the mandate of the exchanges.
What tools and platforms are essential for scalping?
Scalping demands fast execution, so traders need high-speed internet, a low-latency trading platform, real-time market data, and technical analysis tools, which your broker will provide.
How do I manage risk while scalping?
Risk management in scalping involves tight stop-loss orders, proper position sizing, and disciplined trade execution. Avoid overleveraging, use risk-to-reward ratios, and exit losing trades quickly to minimise capital loss.
Is the scalping strategy illegal?
Scalping is legal in most financial markets but may be restricted by some brokers due to its high-frequency nature. Always check broker policies and regulations before implementing this strategy.
How Can You Do Scalp Trading?
To start scalping, open a trading account, choose a liquid asset, set tight stop-loss levels, use technical indicators, and trade with discipline. Consistently refining your strategy and avoiding emotional trading is key to success.
What is the rule of scalping?
The key rule in scalping is to make quick, small profits while limiting losses. Traders must maintain a high trading frequency, follow strict discipline, and never risk more than they can afford to lose per trade.
What are the pros of scalping?
- Scalping allows trading almost any stock, whether the market is going up, down, or sideways.
- Scalpers and intraday traders can make a lot of money if they get their strategies right.
What are the cons of scalping?
- Scalping requires traders to be highly disciplined and control their emotions.
- Since profit margins are low, scalping may not work well for traders with small capital.
- High brokerage costs due to multiple transactions.
What is scalping in trading?
Scalping is an intraday trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from multiple trades by trading small price movements and keeping the stock quantities high. It is one of the shortest-term strategies as trades are squared off within seconds or minutes rather than hours.


