- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
Difference Between Shares and Mutual Funds
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Jul 25, 2025 10:51 AM IST
Summary
- Investment Structure: Shares represent direct ownership in a company, while mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio managed by professionals.
- Risk Exposure: Shares are high-risk due to market volatility and company-specific performance. Mutual funds spread risk across various securities, offering moderated risk levels.
- Return Potential: Shares can offer high returns if the selected stock performs well. Mutual funds may yield lower but more stable returns, depending on the fund’s composition.
- Expert Management: Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers, making them ideal for those lacking market knowledge. Investing in shares requires active research and monitoring by the investor.
- Diversification: Mutual funds inherently provide diversification across sectors and asset classes. Shares lack this unless the investor independently diversifies.
- Liquidity: Shares offer immediate liquidity through stock exchanges. Mutual fund liquidity depends on the fund type—open-ended funds offer better liquidity than closed-ended ones.
- Cost Efficiency: Share trading may incur lower one-time costs. Mutual funds charge management and other ongoing fees, which can impact net returns.
Both mutual funds and the share market are popular investment avenues in India. Both offer the possibility of good returns through capital appreciation, but also come with certain risks. As an investor, you must understand the difference between mutual funds and the share market to make informed investment choices about building your portfolio.
This article outlines what are the differences between shares and mutual funds, the pros and cons of mutual funds, pros and cons of stocks, and how to choose between the two.
What are Shares?
Before we proceed to the differences between mutual funds and the share market, it’s essential to first clarify what shares are. Shares are equity ownership in the issuing company. When you purchase shares of a company, you become a shareholder and attain partial ownership in the company.
Shares are typically issued to raise capital for various purposes like funding new projects and financing operations. Companies first issue shares in the primary market through an initial public offering (IPO). Post IPO, these shares are then traded on the secondary market through stock exchanges like the BSE and NSE.
As a shareholder, you are entitled to a proportional claim over the company’s profits and assets. The performance of your investment is directly linked to the performance of the company and the market demand for its shares. If the company performs well, share prices will rise, resulting in potential capital appreciation. The issuing company may also declare dividends.
What are Mutual Funds?
Now that you know what shares are, let’s briefly understand the concept of mutual funds. Mutual funds are investment instruments that pool money from different investors and invest the pooled corpus into various assets.
Depending on the objective of the mutual fund scheme, it may invest in equity assets (equity funds), debt instruments (debt funds) or a mix of both (hybrid funds). It is important to note that owning units of an equity fund does not give you actual ownership of the underlying asset. In other words, you do not have the same rights and privileges as a shareholder. This is a major difference between mutual funds and shares.
Another significant difference is professional management. Unlike shares, each mutual fund is managed by an experienced fund manager who is responsible for selecting assets, monitoring the fund’s performance, and rebalancing its portfolio to ensure good returns in changing market conditions. You can also use an SIP Calculator to plan and estimate your mutual fund investments, helping you invest systematically with clear financial goals.
With clarity on what mutual funds are, we can now proceed to the detailed analysis of mutual funds vs. shares.
Difference Between Shares vs Mutual Funds
As outlined in the definitions above, both mutual funds and the share market have several dissimilarities. The following table sums up the differences between mutual funds and the share market to help you make better investment decisions.
| Parameter | Shares | Mutual Funds |
| Ownership | Shareholders are partial owners of the company and can vote on essential company matters. | Mutual fund unitholders do not have ownership and voting rights in the company whose shares the fund purchases. |
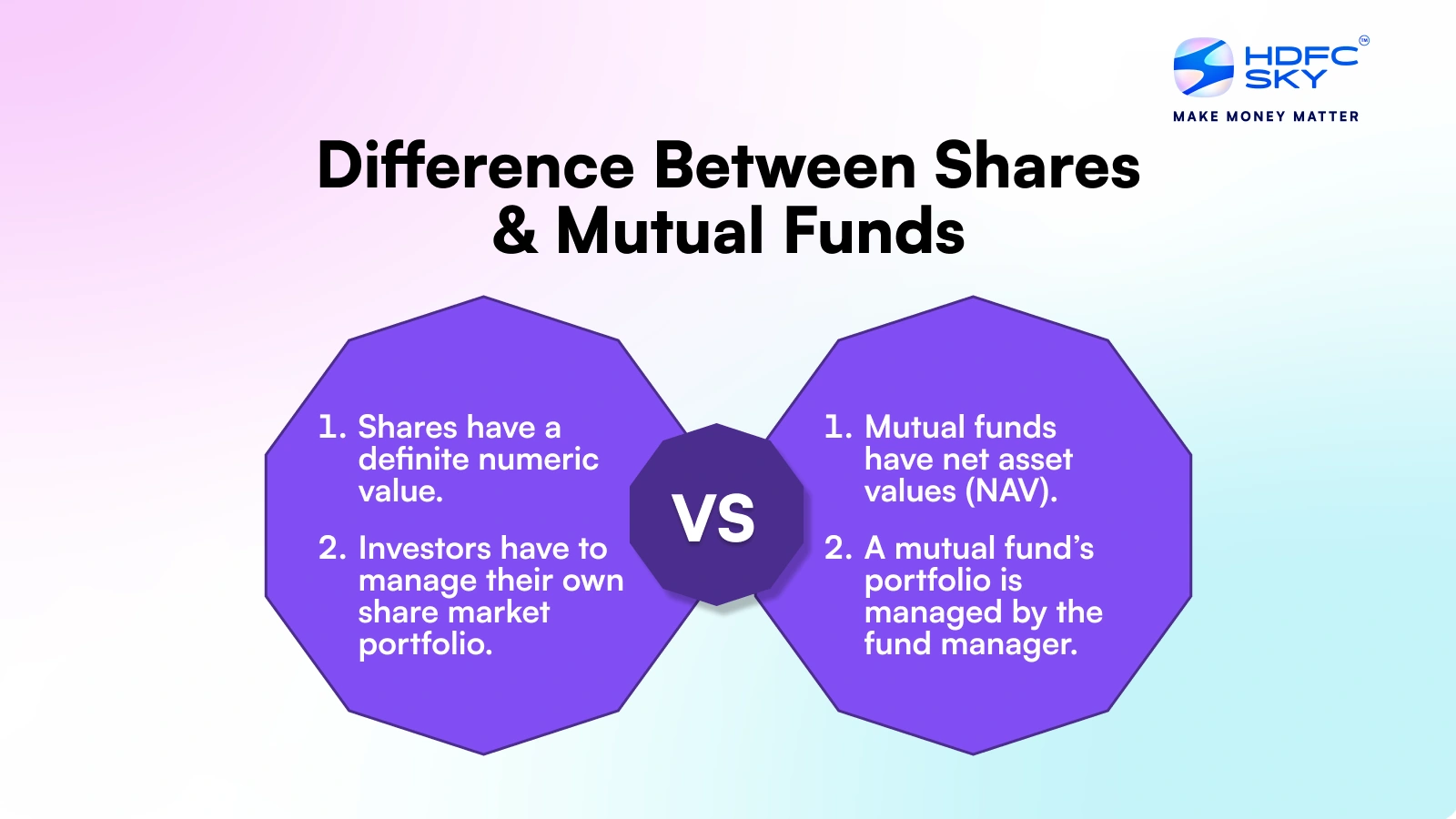
| Numeric Value | Shares have a definite numeric value. | Mutual funds have net asset values (NAV). |
| Risk Level | Riskier since shares are susceptible to market volatility. | Relatively less risky since mutual funds can diversify investments in a basket of securities. |
| Diversification | Shares do not have built-in diversification benefits. You can diversify by investing in companies belonging to different sectors and industries. | Mutual funds invest in a basket of securities offering built-in diversification benefits. |
| Required Market Knowledge | Thorough market knowledge is required for selecting stocks. | Market knowledge is beneficial but less essential since mutual funds are managed by fund managers. |
| Costs | Transaction costs are incurred when buying and selling shares. | Investment fees (expense ratio) are retrieved during the investment. |
| Investment Horizon | Investment can be made for the long-term or short-term duration. | Mutual fund investments perform better in the long run. |
| Tax Benefits | No tax benefits can be claimed. | ELSS (equity-linked savings schemes) funds offer benefits u/s 80(C). |
| Management | Investors have to manage their own share market portfolio. | A mutual fund’s portfolio is managed by the fund manager. |
| Systematic Plans | Not possible. | SIP option available |
While this table represents the major differences between mutual funds and the share market, it’s important to understand that both investment options offer some distinct advantages and disadvantages. Moving forward from the mutual funds vs. shares comparison, we now focus on the pros and cons of each in detail.
Pros and Cons of Shares
Apart from the differences in mutual funds and shares, it’s also critical to understand the pros and cons of stocks. The various pros and cons of stocks listed below can make it easier for you to decide if shares are indeed the right investment option for you.
Pros of Investing in Shares
- Return potential: Investing in shares of growing companies and emerging sectors can offer return potential, especially over a long-term horizon.
- Ownership benefits: One of the major advantages of choosing shares in the mutual funds vs. shares debate is the ownership stake you enjoy. Investing in shares makes you part owner of the company, granting you voting rights on essential decisions like acquisitions and executive appointments.
- Hedge Against Inflation: Historically, shares have offered inflation-beating returns over the long run. Adding shares to your investment portfolio can help preserve the value of your real returns.
- Dividend Income: As a shareholder, you can earn regular income through dividend distribution. Apart from the general capital appreciation in terms of share value, this can be a good source of passive earning.
- Liquidity: Shares are liquid investment instruments since you can easily buy and sell shares on the stock exchange. You can quickly convert your investment into cash if the need arises.
Cons of Investing in Shares
- Volatility: Share prices can fluctuate significantly over the long term as well as in a single day due to various factors like market sentiment and company performance. These fluctuations can impact your total portfolio value and result in short-term losses.
- Market Knowledge Requirement: Investing in shares requires in-depth market knowledge, analysis capabilities, and an understanding of market trends. If you do not possess these qualities, you may incur hefty losses.
- Risk of Loss: Risk is also an important factor to consider when choosing whether to invest in shares vs. mutual funds. If you invest in shares, the probability of losing your entire investment can be high, if the company underperforms or goes bankrupt.
- No Assured Returns: Unlike fixed-income assets like fixed deposits, shares do not offer guaranteed returns. Returns are purely based on the performance of the stock.
- Taxes and Brokerage: Investment in shares is subject to capital gains tax (based on the holding period) and the securities transaction tax. Dividend income is also taxable. Additionally, you have to pay brokerage fees for each trade. All this can eat your total earnings from the investment.
Pros and Cons of Mutual Funds
Understanding the pros and cons of mutual funds can make it easier to grasp the difference between mutual funds and the share market. We have listed the pros and cons of mutual fund investing below.
Pros of Mutual Funds
- Built-in Diversification: A major difference between mutual funds and the share market is that mutual funds invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other money market instruments to hedge risks associated with a single stock, sector, or asset class.
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are professionally managed by experienced fund managers. They are responsible for selecting the assets for investment, monitoring it, and rebalancing the portfolio according to the fund’s objectives to maximise returns for the investors.
- Affordability: Another difference between mutual funds and the share market is the affordability aspect. Mutual funds allow investors to begin with nominal investments via systematic investment plans (SIPs), making it easier for small investors to partake in diversified investment opportunities.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds are highly liquid investments since investors can sell their units at the current NAV and redeem their investments at any time.
- Tax Benefits: Investors can claim tax benefits of up to Rs. 1.5 Lakhs under Section 80(C) of the Income Tax Act by investing in ELSS funds. This can help them lower their overall tax liability.
Cons of Mutual Funds
- Investment Costs: Mutual funds charge administration and management fees in the form of an annual expense ratio. This ratio can vary from 0.80%-2.25% of the daily net assets. Expense ratio charges can affect your returns over time.
- Market Risk: While mutual funds are less riskier than shares, they still carry a certain degree of market risk. Fluctuations in the market can impact the value of the fund’s underlying assets. So, if the market underperforms, investors may have to bear losses.
- Lack of Control: A key difference between mutual funds and shares is the aspect of control. The fund manager makes investment decisions as per the fund’s objectives and market conditions. Individual investors have no control over the investment decisions.
- Exit Fees: Mutual funds charge an exit fee if the investor exits the fund before a specified time period. This fee can limit the liquidity benefits of mutual funds to a certain extent.
Why Some Prefer Mutual Funds Over Individual Stocks
Beginner investors often face the same dilemma: Should I invest in mutual funds or stocks? Based on the differences between mutual funds and shares, many tend to side with mutual funds (MFs) in the mutual funds vs. share market debate. Investors prefer MFs over shares for the following reasons:
- Passive Management: Investing in stocks requires active management, market analysis, and trend tracking. If you have limited time, this can become challenging. However, when you invest in mutual funds, you can pass on the burden of asset selection, timing trades, and monitoring their progress to the fund manager. This significant difference between mutual funds and shares makes MFs ideal for passive investors.
- Diversification Perks: If you wish to build a diversified share market portfolio, you will have to invest in multiple stocks from varied sectors and market capitalisations. Since mutual funds invest in a varied basket of securities, they offer instant diversification benefits, and you get exposure to a broad range of securities without having to individually select stocks.
- Professional Management Benefits: From the shares vs. mutual fund comparison highlighted above, it’s clear that you need market knowledge and expertise to make stock market investments. Beginners generally lack such market knowledge, which makes them more susceptible to losses. In the case of mutual funds, professional and experienced fund managers make investment decisions, making them most suited for beginners with limited market knowledge.
- Reduced Investment Costs: Stock market trading is often linked to relatively high brokerage fees and transaction costs. Moreover, building a diversified portfolio means investing in 20-25 different stocks, resulting in a high initial investment. Investment costs of MFs are capped at a fixed rate (expense ratio). Additionally, since mutual funds pool funds from different investors to invest in a diversified basket of assets, you can tap into diversification benefits at a comparatively lower cost.
Conclusion
Every investor must understand the differences between mutual funds and shares to make informed decisions. The above discussion highlighted what is the mutual funds vs. shares debate, focusing on the pros and cons of stocks as well as the pros and cons of mutual funds. In a nutshell, the differences between mutual funds and shares sum up how each investment instrument caters to different investor preferences. While professionally managed mutual funds help investors tap into the benefits of high returns without having to select stocks individually, shares offer direct equity ownership in a company. Ultimately, deciding whether to invest in mutual funds vs. stocks entirely depends on your investment goals, risk appetite, and market knowledge.
Related Articles
FAQs on Difference Between Shares and Mutual Funds
What is the lowest amount that needs to be invested in shares and mutual funds?
There is no minimum amount for stock trading in India. For mutual funds, the minimum lump-sum investment threshold is set at Rs. 100, while the minimum threshold for SIPs is at Rs. 500.
Can I make an investment of ₹100 in mutual funds?
Yes. You can invest a lump-sum of Rs. 100 in a mutual fund, subject to the specific terms of the scheme. However, for SIP investments, the minimum contribution limit is Rs. 500.
Are mutual funds affected by the stock market?
Yes. Price volatility of shares in the stock market influences the NAV of mutual fund units, thereby impacting returns.
How long should you invest in a mutual fund?
The ideal investment duration will depend on your goals, return expectation, and the type of fund in question. Generally, investing with a long-term perspective of at least 5-10 years is considered ideal to ride out short-term volatility and benefit from compounding returns.
What are the different types of shares?
Shares can be broadly classified into two categories: equity and preference shares. The former offers shareholders ownership rights, dividend payments based on the company’s performance, and voting privileges while the latter offers fixed dividend, but no voting rights. Each can be further classified into bonus, sweat equity, authorised share capital (for equity shares) and cumulative, non-cumulative, participating, non-participating, convertible, non-convertible shares (preference shares).
Is SIP 100% safe?
As market-linked investments, SIPs are not 100% safe. They are subject to market risks. However, they are safer than investing in individual shares. SIPs offer the benefit of rupee-cost averaging and diversification to hedge risks and offer good long-term returns.


