- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
Different Types of IPOs? Fixed Price vs Book Building
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Sep 8, 2025 03:12 PM IST
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process through which a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time. Understanding the different types of IPOs is essential for investors to make informed decisions. Each type be it Fixed Price, Book Building or distinct methods of pricing and share allocation.
What is an IPO?
An IPO (Initial Public Offering) is the process by which a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time to raise capital. It marks the company’s transition from private to publicly traded allowing investors to buy ownership in the business through the stock market.
Types of IPO
As mentioned above there are two types of IPOs , Fixed Price Issues and Book Building Issues. Let us understand the two IPO types in detail:
1. Fixed Price Issue
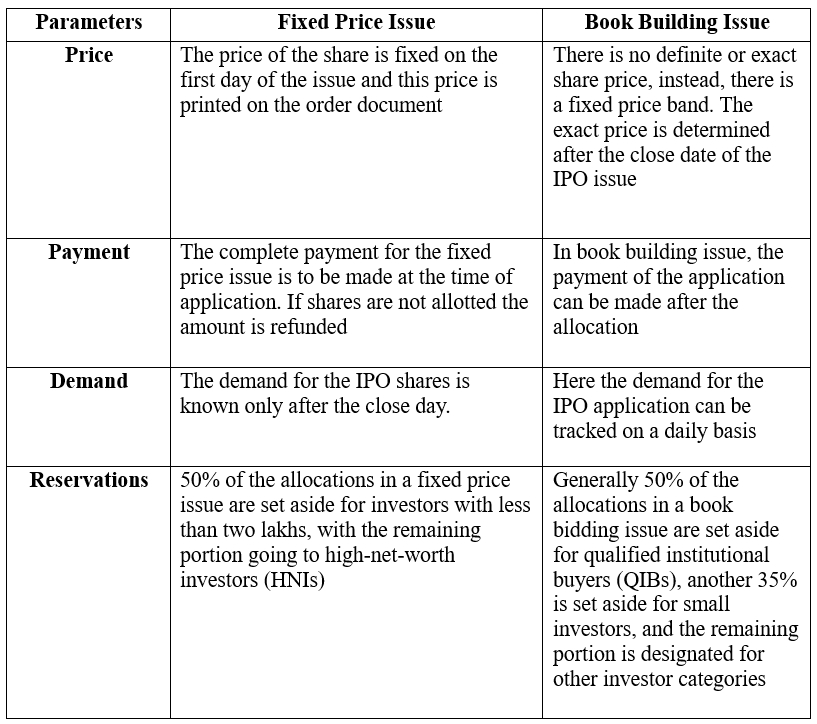
In a Fixed Price Issue the IPO issuing company decides the issue price before going public offering shares to investors at a fixed price. This price is determined by the issuing company with the help of the underwriters they hire. The price is based on factors such as the company’s financial performance, industry trends and market conditions. Investors applying for shares in a Fixed Price Issue know the exact price at which they will be allotted shares if their application is successful. This method provides transparency and simplicity, making it easier for retail investors to participate. However, the Fixed Price Issue may not always reflect the true market value of the shares, as the price is set without considering investor’s demand for the company’s shares . Additionally, there is a risk that the shares may be underpriced or overpriced affecting investor returns in the secondary market.
Example of Fixed Price Issue:
Suppose a company decides to raise funds by issuing shares at a fixed price of ₹100 per share. Investors can subscribe to the IPO knowing exactly what price they will pay, regardless of demand or market conditions.
2. Book Building Issue
In a Book Building Issue the IPO issuing company does not fix a price but instead indicates a price range within which investors can bid for the shares. The bidding process takes place over a specified period during which both institutional and retail investors submit their bids and share the number of shares they wish to purchase along with the price they are willing to pay. Based on the bids received the final price is determined through a process of price discovery during the IPO process. This method allows for better price discovery and market participation as investors’ bids help determine the final price. It also allows the issuer to capture the true market demand for its shares. However the Book Building process can be complex and may exclude smaller investors who are unable to participate in the bidding process.
The concept of the book-building issue is relatively new in India. It was introduced by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1995 to streamline the capital market and overcome the issues of high pricing .
Example of Book Building Issue:
A company launches an IPO with a price band of ₹90 to ₹110 per share. Investors place bids within this range during the subscription period. Based on demand, the final issue price is determined, say ₹105 and shares are allotted accordingly.
Note that apart from the above two common types of IPOs, there is also a third type of IPO called Dutch Auction IPO, which is relatively less popular in the Indian stock market. In this type of IPO, investors place bids stating the number of shares they want and the price they are willing to pay. The price starts high and decreases until the bid matches the number of shares offered by the company.
Difference Between Fixed Price and Book Building Issue IPO
To help you better understand the difference between the two types of IPO, we are listing below the differences between the two. Depending on your goal, and how you manage uncertainty, understanding the primary differences between the two will help you make better-informed decisions.
Advantages of Fixed Price Issue IPO and Book Building IPO
Here are the advantages of both Fixed Price Issue IPO and Book Building IPO
Advantages of Fixed Price Issue IPO
- Price Transparency: Investors know the exact price of the shares before applying.
- Simplicity: Easier for new investors to understand and participate.
- Suitable for Retail Investors: Offers clear cost visibility and planning.
Advantages of Book Building IPO
- Market-Driven Pricing: Helps in discovering the right price through investor demand.
- Efficient Allocation: Shares are allocated based on bids making the process more competitive.
- Better Valuation: Reduces underpricing or overpricing risks for the company.
Disadvantages of Fixed Price Issue IPO and Book Building IPO
Here are the disadvantages of both Fixed Price Issue IPO and Book Building IPO:
Disadvantages of Fixed Price Issue IPO
- No Price Determination: The company sets the price without knowing actual market demand.
- Under/Overvaluation Risk: Shares might be overpriced or underpriced affecting both issuer and investors.
- Lower Flexibility: Does not adjust to real-time demand during the offer period.
Disadvantages of Book Building IPO
- Complex for Retail Investors: The bidding process may confuse or deter new investors.
- Uncertain Allotment: Investors don’t know if they’ll receive shares until after allocation.
- Requires Greater Transparency: The issuer must provide detailed and frequent disclosures.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of IPOs is crucial for investors looking to participate in a company’s public listing. While Fixed Price IPOs offer simplicity and price clarity, they may not always capture the true market value of shares. On the other hand, Book Building IPOs provide a more dynamic and demand-driven pricing method but can be complex for new investors. The choice between the two depends on factors such as risk appetite, market knowledge and investment goals. By carefully evaluating these IPO types, investors can make informed decisions, while companies can select the most suitable approach to raise capital effectively.
Related Articles
FAQs on Types of IPOs
What is Book Building IPO?
A Book Building IPO is a process where the price of the shares is not fixed in advance. Instead, investors place bids within a price range (price band), and based on demand, the final issue price is decided.
What is fixed issue IPO?
A Fixed Price IPO is an initial public offering where the company sets a fixed price per share before the subscription begins. Investors know the exact price at which they can buy the shares, making the process straightforward and transparent.
How many types of IPOs are there?
There are two types of IPOS – Fixed Price Issues and Book Building Issues. These two IPOs vary as to how the issue price is determined.
What is the most common type of IPO?
Both types of IPOs are equally preferred in the Indian stock market. The IPO issuing company decides what type of IPO they will go ahead with.
What type of market is IPO?
IPO is a primary market where shares of a company are offered and bought for the first time by the general public
Which IPO is best currently?
There is no such IPO which is best depending on its type. Whether an IPO is good or bad depends on the company’s growth potential, financial health and market sentiments.


