- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is an NRO Account?
- Why Do You Need to Open an NRO Account?
- How to Open NRO Accounts? – Documentation Requirements
- Eligibility Criteria to Open an NRO Account
- Features of an NRO Account at a Glance
- Understanding Deposits in an NRO Account
- Permissible Credits for NRO Accounts
- Permissible Payments in India from the NRO Account
- Repatriation for NRO Accounts
- Tax Rules for Interest Income from NRO Account
- Benefits of an NRO Account
- Limitations of NRO Accounts
- Conclusion
- FAQs on NRO Account
- What is an NRO Account?
- Why Do You Need to Open an NRO Account?
- How to Open NRO Accounts? – Documentation Requirements
- Eligibility Criteria to Open an NRO Account
- Features of an NRO Account at a Glance
- Understanding Deposits in an NRO Account
- Permissible Credits for NRO Accounts
- Permissible Payments in India from the NRO Account
- Repatriation for NRO Accounts
- Tax Rules for Interest Income from NRO Account
- Benefits of an NRO Account
- Limitations of NRO Accounts
- Conclusion
- FAQs on NRO Account
NRO Account: Meaning, Features & Documentation
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Jul 25, 2025 12:44 PM IST
Summary
- NRO Account Defined: A Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) account is designed for NRIs to manage income earned in India, such as rent, dividends, pensions, or other sources.
- Primary Purpose: It enables NRIs to deposit and manage rupee income earned within India while residing abroad.
- Repatriation Rules: Funds in an NRO account are non-repatriable by default, though up to USD 1 million per financial year can be repatriated after paying applicable taxes and completing formalities.
- Joint Holding & Operations: Can be opened jointly with Indian residents or other NRIs, offering flexibility in account management.
- Taxation: Interest earned in NRO accounts is subject to TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) as per Indian income tax laws.
- Account Types: Available in savings, current, recurring, or fixed deposit formats.
- RBI Compliance: Fully regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and requires submission of NRI status proofs for activation.
- Key Distinction: Unlike NRE accounts, NRO accounts handle earnings within India and are ideal for managing domestic income and payments.
Cross-border financial management can be difficult for a Non-Resident Indian who is dealing with income earned in India. This is when a Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) account comes in handy. An NRO account is designed for NRIs purely and allows the seamless management of your earnings in India while complying with tax and regulatory obligations.
Whether it is rental income, dividends, or pension, it is very easy to transact with this account. It relies on Indian laws for compliance purposes. In this article, we will look into all the essentials regarding NRO accounts, including features, benefits, and necessary documentation.
What is an NRO Account?
An NRO account or a Non-Resident Ordinary account is a rupee-denominated bank account designed mainly for non-resident Indians (NRIs). Its main purpose is the management of NRIs’ income from India, like interest, dividends, and any other earnings. Note that NRO account is for managing earnings. In case an NRI wants to invest in Indian securities market, he/she invariably has to open a Demat account which cane be done using a Demat account app.
An NRO bank account also allows money transfers into India through foreign locations. Furthermore, you can deposit money in Indian rupees and foreign currencies into the account. However, withdrawals cannot be made in any foreign currency from NRO accounts. This convenience in managing finances makes it easy for NRIs wanting to settle in India.
Why Do You Need to Open an NRO Account?
According to FEMA guidelines, NRIs cannot open regular savings accounts in India that are meant for Indian citizens. Hence, when they declare the NRI status, their earlier savings account transforms into a Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) account through which they manage their Indian incomes effectively.
Moreover, it supports investments in India, making it especially useful for NRIs with income-generating assets. The account ensures that the regulations are complied with while providing a convenient banking solution for managing finances in the country effectively.
How to Open NRO Accounts? – Documentation Requirements
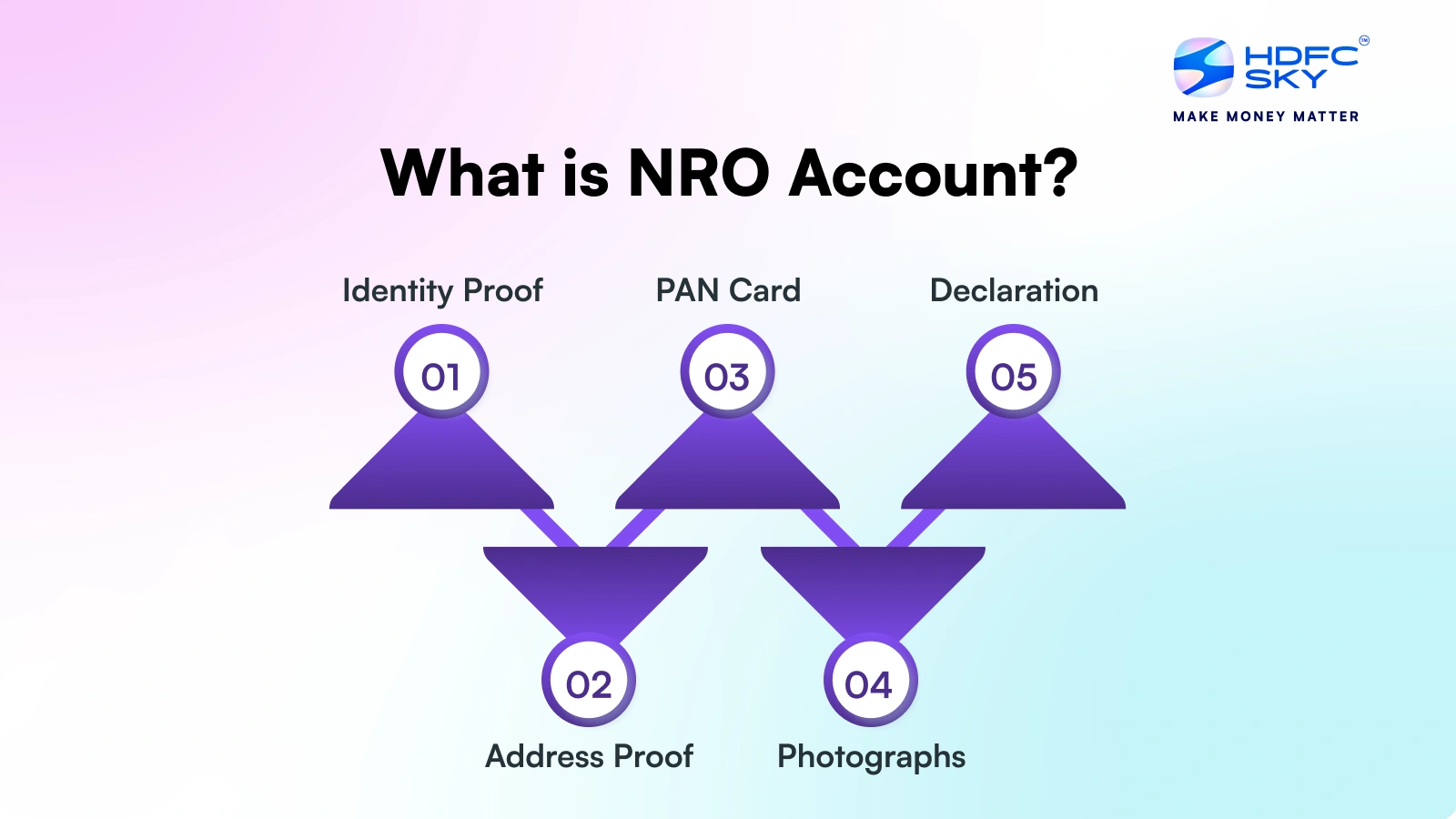
After understanding the meaning of an NRO account, you must know the documents required to open this type of account. To open an NRO account, you need to provide certain documents to the bank. Typically, these include:
- Identity Proof: A passport with a valid visa or residence permit
- Address Proof: Documentation for both overseas and Indian addresses, if applicable
- PAN Card: Required for tax purposes
- Photographs: Recent passport-sized photos
- Declaration: A signed declaration under FEMA regulations confirming your NRI status
In addition, banks may request extra NRO account opening documents, such as Form 60, if you do not have a PAN, proof of income or other declarations.
Eligibility Criteria to Open an NRO Account
To open an NRO account, you must fulfil the following NRO account eligibility criteria:
- Be a non-resident Indian or a Person of Indian origin
- Someone generating earnings in Indian rupees
- Individuals or entities from Pakistan or Bangladesh, with prior approval of the RBI
- Individuals or entities from Pakistan or Bangladesh belonging to minority communities who are residing in India
- Any NRI holding a joint account with a resident Indian
Features of an NRO Account at a Glance
The following are the NRO account details that you must go through to understand more about this banking account:
- As an NRI, you can transfer both interest and principal from your NRO account to your account in your country of residence.
- Depositors may submit a request for the transfer of an amount of not more than USD 1 million in a fiscal year, provided they are assessed for the payment of tax.
- The NRO tax rate applicable is 30% plus applicable surcharge and cess to an NRO account and is deducted at the source.
- An NRO account may be credited with rental income, pension income, dividend income, etc.
- Loans can be taken against NRO accounts by NRIs.
- NRO accounts can be opened as savings as well as a current bank account.
- NRO accounts can be operated worldwide through internet banking, and NRO account holders receive international debit cards.
- Joint NRO accounts are allowed for two or more individuals in which one holder must be an NRI, PIO or OCI. However, the second holder can be a resident of India. If both holders are living abroad, they can authorise an Indian with the power of attorney to operate their account.
- An NRO account allows the nomination facility to appoint beneficiaries in the event of the depositor’s death.
- Through the NRO accounts, it is possible to invest in NRO account mutual funds, term deposits, recurring deposits, etc. The Indian Government guarantees term deposits of up to ₹5,00,000.
- According to RBI regulations, you can transfer money to an NRE account from an NRO account by following specific guidelines.
Understanding Deposits in an NRO Account
Funds coming from India or income earned within the country can be credited to an NRO account. Some of the most significant categories of cash deposits in NRO accounts, according to RBI guidelines, include:
-
Current Income
This category will include rental income, dividends from investments, pensions, and interest earned from fixed deposits (FD) and bank accounts in India. All funds from current income are fully repatriable to an overseas account without an NRO account limit.
-
Capital Income
This includes the maturity proceeds of FDs, sale proceeds of property, and redemption of mutual funds or shares. You can repatriate funds of up to USD 1 million per financial year (April–March) across all your NRO accounts in India. Transfers from your NRO account to your NRE account also count toward this USD 1 million limit.
In addition, the income or funds brought from abroad in foreign currency can be deposited into an NRO account. Such funds will be converted into Indian rupees based on current currency conversion rates, and you can withdraw it in Indian currency. Importantly, there is no upper limit on the total amount that can be deposited into NRO accounts.
Permissible Credits for NRO Accounts
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) permits the following credits into an NRO account:
- Income generated in India, such as rent, dividends, pensions, and interest from deposits
- Transfers from another NRO account
- Direct remittances from abroad deposited into the NRO account
- Proceeds from the sale of property or other assets located in India
Permissible Payments in India from the NRO Account
The RBI guidelines for NRO accounts allow NRIs to make several types of payments within India, such as:
- Payment of utility bills, insurance premiums and equated monthly instalments (EMIs)
- Investment in shares, mutual funds and other securities using funds from your NRO account
- Payment of taxes, statutory dues, and other government charges
Repatriation for NRO Accounts
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) establishes the legal framework governing fund repatriation for NRIs from India. Under FEMA regulations, NRIs can repatriate up to USD 1 million per financial year from their NRO accounts. However, you must seek approval from the Reserve Bank of India if the principal amount is beyond USD 1 million.
It can include various income sources such as rents, dividends or pensions earned in India, provided that all applicable NRO account taxation has been settled.
Tax Rules for Interest Income from NRO Account
An NRO account holder has to pay tax on any income generated in India. The NRO account tax income might come from such sources as:
- Capital Gains: Taxes on profit from investments made within India.
- Consulting Fees or Salary: Earnings from the services provided or as an employee in India.
- Rental Income: Income from properties owned in India.
- Interest Income: Interest earned on money kept in an NRO account or other investments.
For NRO accounts, the TDS rate is 30%, besides any appropriate cess or surcharges that may apply. The interest earned on an NRO account will be deducted at the source by your bank where you maintain an NRO account. In this way, the bank deducts and credits the tax to the government before passing the balance to your account.
Understanding these tax implications is very important for NRIs to be in compliance and have effective financial planning while managing their investments in India.
Benefits of an NRO Account
Here are some of the NRO account benefits you can enjoy upon opening this account:
-
Safeguarding Earnings
Non-resident individuals can earn income from domestic sources, such as rental income from properties and dividends from stock market investments. These funds must be deposited into financial institutions through an NRO account, ensuring the secure management and safekeeping of all earnings accrued within India.
-
Increased Credit Availability
NRIs can obtain loans against their NRO fixed deposits to cover emergency expenses in India or their country of residence. Since these loans are secured by the collateral of the NRO deposit, they typically offer significantly lower interest rates compared to unsecured loan options.
-
Multiple Account Holders
An NRO account can be jointly opened by two or more individuals. At least one account holder must be an NRI, PIO, or OCI, while the other can be an Indian resident. If both reside abroad, they can appoint someone in India with the power of attorney to manage their accounts.
-
Ease of Investment
NRO accounts facilitate easy investments in term deposits that provide safe and assured returns, including fixed and recurring deposits. In addition, these fixed deposit accounts are insured up to ₹5 lakh by the Government of India, ensuring security and high returns on investments made through NRO accounts.
Limitations of NRO Accounts
Here are some NRO account restrictions you must be aware of before opening this account:
-
Tax Implications
Interest earned on NRO accounts is liable to a 30% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS). Therefore, NRIs must pay taxes on the income generated in India, which can substantially reduce the overall returns on their investments and impact financial planning.
-
Limited Use for Foreign Income
NRO accounts cannot accept deposits of income earned outside India. Thus, NRIs have to maintain separate accounts, such as NRE accounts and FCNR accounts, to manage their foreign earnings, which complicates the management of finances in different currencies and jurisdictions. This limitation can create additional challenges for effective budgeting and investment strategies.
Conclusion
An NRO account is crucial for NRIs to effectively manage their income from India while complying with local regulations. It provides numerous benefits, including convenient fund management and investment opportunities. However, it has certain limitations, such as taxation and restricted repatriation.
Understanding the features and rules governing NRO accounts is essential for NRIs to make informed financial decisions. By leveraging the advantages and addressing the associated challenges, NRIs can ensure smooth and effective management of their financial interests in India.
Related Articles
FAQs on NRO Account
What is the NRO account and its benefits?
An NRO account is a savings or current account held by Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) in India to manage domestically earned income, such as rent, dividends, and pensions. Its benefits include secure fund management, investing in Indian markets, and compliance with Indian regulations.
How much money can I deposit in my NRO account?
There is no upper limit on the amount of money that can be deposited into an NRO account. NRIs can deposit funds from various sources, including rental income, dividends, and foreign remittances, ensuring that all domestic earnings are managed effectively.
What is the withdrawal limit of NRO accounts?
NRO accounts do not have a specific withdrawal limit. However, repatriation of funds abroad has a limit of USD 1 million per financial year. To withdraw an amount above $1 million, the permission of RBI is needed. Withdrawals can be made in Indian Rupees, and there are no limits on local transactions within India.
What is the disadvantage of NRO?
One major disadvantage of NRO accounts is that the interest earned is subject to a 30% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS), which can significantly reduce overall returns. Moreover, these accounts cannot hold foreign currencies.
Is NRO tax-free?
No, NRO accounts are not tax-free. The interest earned on these accounts is subject to income tax in India at a rate of 30%, along with any applicable cess and surcharges. NRIs must comply with tax regulations for income generated within India.
What is the minimum balance for a NRO account?
The minimum balance requirement for an NRO account varies by bank and account type. Generally, banks may require a minimum balance ranging from ₹10,000 to ₹25,000. It is advisable to check with the specific bank for their requirements.
What is the penalty for not converting to an NRO account?
Failure to convert a regular savings account to an NRO account after becoming a Non-Resident Indian may result in penalties imposed by banks. Moreover, it can lead to complications regarding fund management and compliance with regulatory requirements under FEMA guidelines.
Is it mandatory to convert a bank account to NRO?
Yes, NRIs must convert their regular savings accounts into NRO accounts upon changing their residency status. This conversion ensures compliance with FEMA regulations and allows NRIs to manage their income earned in India effectively.


