- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is a Fund Manager?
- Who is a Fund Manager?
- Role of Fund Manager
- Qualities of Fund Managers?
- Types of Fund Managers
- Difference Between Active Fund Managers Vs. Passive Fund Managers
- How to Evaluate a Fund Manager?
- How Do Fund Managers Identify Investment Opportunities?
- What Should You Do When a Fund Manager Changes?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is a Fund Manager?
- What is a Fund Manager?
- Who is a Fund Manager?
- Role of Fund Manager
- Qualities of Fund Managers?
- Types of Fund Managers
- Difference Between Active Fund Managers Vs. Passive Fund Managers
- How to Evaluate a Fund Manager?
- How Do Fund Managers Identify Investment Opportunities?
- What Should You Do When a Fund Manager Changes?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is a Fund Manager?
What is a Fund Manager? Meaning, Role and Types
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Oct 27, 2025 06:00 PM IST
A fund manager is a qualified financial professional who manages investments on behalf of individuals or institutions. Their main job is to decide where and how to invest a fund’s money to meet its goals while balancing risk and return. In mutual funds, the fund manager’s skill directly impacts how your investments perform.
What is a Fund Manager?
A fund manager meaning refers to a professional who oversees and manages investment portfolios on behalf of clients or institutions. The fund manager is responsible for making strategic investment decisions, analysing market trends and aiming to maximise returns while managing risks. They play a key role in the performance of mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds and other investment vehicles.
Who is a Fund Manager?
A mutual fund manager is a professional responsible for handling a mutual fund’s portfolio, choosing where to invest based on research and risk assessment. These experts play a central role in fund management, selecting assets like stocks, bonds and other securities to align with the fund’s objectives. Understanding what is fund management helps investors appreciate how such decisions directly impact return Fund managers for mutual funds are financial experts and decide where, when and how much is to be invested so that the overall objective of the scheme can be achieved.
Mutual fund managers work for Asset Management Companies (AMCs) that launch various mutual fund schemes in India. Fund managers apply their market knowledge to analyse trends, evaluate financial instruments and guide the fund’s performance. Their role in mutual fund management ensures investor money is strategically invested for growth or income, depending on the scheme’s goals. Once done, they manage the portfolio of the scheme accordingly. Their main aim is to maximise profits for the investors while minimising risk as much as possible. Essentially, they are the experts you are paying to research, analyse and invest your pooled money effectively.
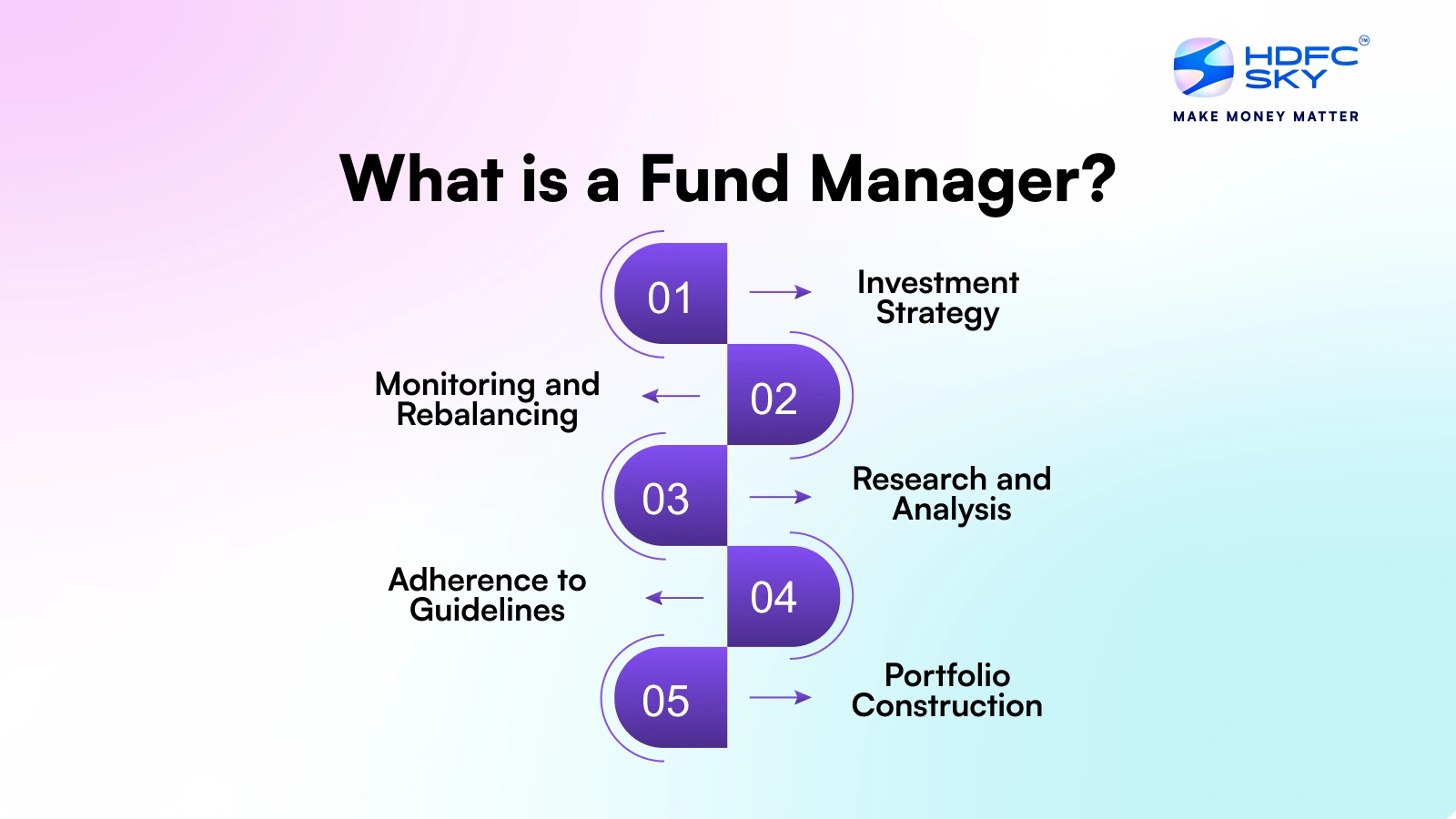
Role of Fund Manager
A fund manager plays a vital role in the performance and management of a mutual fund. They are responsible for making key investment decisions based on research, market trends and financial analysis.
- Portfolio Management: Selecting and managing the mix of stocks, bonds or other assets.
- Research & Analysis: Studying market data, company performance and economic indicators.
- Risk Management: Ensuring investments align with the fund’s risk profile and objectives.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly tracking and adjusting the portfolio to maximise returns.
- Compliance: Adhering to SEBI regulations and internal fund policies.
Qualities of Fund Managers?
A successful fund manager combines skill, discipline and insight to deliver consistent returns. Their effectiveness is key to investor confidence and fund performance.
- Analytical Thinking: Ability to interpret financial data and market trends.
- Strong Decision-Making: Makes informed timely investment decisions under pressure.
- Experience & Expertise: Deep understanding of markets, sectors and financial instruments.
- Discipline: Sticks to the fund’s strategy and avoids impulsive moves.
- Transparency: Communicates clearly with investors about fund performance and strategy.
- Adaptability: Adjusts to changing market conditions effectively.
- Integrity: Upholds ethical standards and prioritises investors’ interests.
Types of Fund Managers
As there are numerous types of mutual fund schemes fund managers are also classified based on the type of mutual fund scheme they manage. Here are the types of fund managers in India:
1. Active Fund Managers
Active fund managers actively buy and sell assets to manage the portfolio in real-time. They are actively involved in ensuring that the fund can achieve its objective and provide good returns to the investors.
What they do:
- Study assets based on their technical and fundamental aspects, industry trends and market conditions.
- Actively buy and sell securities to adjust the portfolio of the mutual fund scheme.
2. Passive Fund Managers
Passive fund managers are not active in managing the portfolio of the mutual fund scheme. They mirror the performance of a market index such as the Sensex or Nifty without trying to make higher returns than the benchmark.
What they do:
- Create and manage the scheme’s portfolio to mirror the performance of an index.
- Make changes in the portfolio only when there is a change in the underlying index.
3. Fund of Fund Manager
A Fund of Fund manager pools money from various investors to invest in a portfolio of other investment funds, such as mutual funds or hedge funds. They create a portfolio of such funds and manage it accordingly.
What they do:
- Create and manage a portfolio of multiple investment funds.
- Make changes to the included funds to ensure minimum risk and maximum profit.
Difference Between Active Fund Managers Vs. Passive Fund Managers
Active and passive fund managers follow distinct approaches to managing investments. Active managers aim to beat the market through research and trading, while passive managers replicate market indexes for steady returns.
| Aspect | Active Fund Managers | Passive Fund Managers |
| Approach | Conduct in-depth research to beat the market | Track a market index or benchmark |
| Trading Frequency | Frequent buying and selling of securities | Buy-and-hold strategy with minimal trading |
| Goal | Aim for higher returns than the benchmark | Match market performance |
| Cost | Higher management fees due to active trading | Lower fees due to minimal management |
| Risk | Higher risk due to market timing and stock selection | Lower risk as portfolio mimics index |
| Flexibility | Flexible to adjust portfolio based on market trends | Rigid portfolio tracking index |
How to Evaluate a Fund Manager?
Choosing the right fund manager is essential for long-term investment success. Evaluating their performance, style and risk management helps ensure better returns.
- Track Record: Review the fund manager’s past performance across different market cycles.
- Consistency: Look for stable and consistent returns rather than short-term spikes.
- Investment Style: Understand their investment philosophy (value, growth, blend, etc.).
- Risk Management: Assess how well the manager controls risk during market volatility.
- Experience & Credentials: Consider their industry experience, qualifications and past firms.
- Fund Performance vs Benchmark: Check if the fund consistently outperforms its benchmark.
- Portfolio Turnover: Higher turnover may lead to increased transaction costs and taxes.
- Transparency: Managers who clearly communicate strategies and portfolio choices build trust.
- Reputation: Check for market reputation, reviews and regulatory compliance.
- Fund Size: Extremely large funds may struggle with agility in investment decisions.
How Do Fund Managers Identify Investment Opportunities?
Here is how fund managers identify investment opportunities and include securities in the portfolio of a mutual fund scheme:
- Market fluctuations: The stock market and all other markets see regular changes in the prices of their securities. The mutual fund managers find such changes in price and identify undervalued investments that can provide future profits.
- Macroeconomic Analysis: Studying broader economic trends, interest rates, inflation, regulatory changes and global events that could impact market sectors or specific companies.
- Industry Analysis: Fund managers in mutual funds analyse the performance of various industries and sectors, along with the securities within them. They include securities in the portfolio if they feel they can provide long-term returns.
- Financial Performance: The fund managers research and evaluate various securities based on their financial performance. They add securities that have consistently performed better.
- Meetings and Research: Interacting with company management, industry experts, and utilising research reports from in-house or external analysts.
This rigorous process helps the mutual fund portfolio manager select securities that they believe will contribute positively to the fund’s performance, aligning with the fund’s investment objective.
What Should You Do When a Fund Manager Changes?
When a fund manager exits, investors should stay calm and evaluate the situation before taking action. Manager changes are common and not always negative.
- Review Fund Performance: See if the new manager maintains consistency.
- Understand the Reason for Exit: Check if it’s voluntary or due to poor performance.
- Assess the New Manager: Look into their experience, strategy and past performance.
- Wait and Watch: Avoid making impulsive decisions monitor changes for a few quarters.
- Diversify Investments: Spread investments across funds to reduce reliance on a single manager.
Conclusion
A fund manager plays a crucial role in determining the success of a mutual fund. Their expertise, research skills and decision-making ability directly impact the fund’s performance and investor returns. Whether managing an active or passive fund, the fund manager’s goal remains the same to align investments with the fund’s objectives while balancing risk and reward. For investors, understanding the role and qualities of a good fund manager helps in choosing the right mutual fund and building long-term wealth through informed investment decisions.
Related Articles
FAQs on What is a Fund Manager?
What are some key responsibility of fund manager in mutual fund?
A fund manager is responsible for selecting and managing the right mix of investments to meet the fund’s objective. This includes analysing market trends, picking suitable stocks or bonds, balancing risk, and making timely portfolio adjustments. They ensure the fund follows SEBI rules and regularly track performance against benchmarks.
What is the tenure of a fund manager?
The tenure of a mutual fund manager is not fixed. As they are employed by the AMC, they can work as long as the AMC employs them.
How do I choose a fund manager for a mutual fund?
You can choose an ideal mutual fund manager by comparing their experience, investment style, past performance and qualifications.
Is it good to have a fund manager?
Yes, a good fund manager can increase your return potential and help protect your capital in the event of a market crash or any other negative market situation.
What is the qualification for a mutual fund manager?
Most fund managers have professional qualifications in the field of finance, economics, or an MBA, and certifications like CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst).
Can a fund manager change the nature of mutual funds?
No, they must stick to the fund’s objectives and are not allowed to change the nature of the mutual funds.
What are the steps to be taken after a fund manager’s exit?
If the fund manager has exited the scheme, the AMC will employ a new fund manager. You should check the qualifications and past performance of the new fund manager and ensure that the appointment does not negatively affect the scheme’s returns.
Who appoints a fund manager?
The Asset Management Company (AMC) appoints the fund manager. They select professionals based on qualifications, experience, and track record.


