- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is Futures Trading in Share Market?
- How Futures Trading is Different From Other Financial Instruments?
- How Future Trading Works
- How to Trade Futures in India?
- Examples of Futures Trading
- Types of Futures Trading
- Difference Between Options and Futures Trading
- Why Should You Invest in Futures Trading?
- Advantages of Futures Trading
- Disadvantages of Futures Trading
- Regulation of Futures
- Things to Keep in Mind While Trading Futures
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Futures Trading
- What is Futures Trading in Share Market?
- How Futures Trading is Different From Other Financial Instruments?
- How Future Trading Works
- How to Trade Futures in India?
- Examples of Futures Trading
- Types of Futures Trading
- Difference Between Options and Futures Trading
- Why Should You Invest in Futures Trading?
- Advantages of Futures Trading
- Disadvantages of Futures Trading
- Regulation of Futures
- Things to Keep in Mind While Trading Futures
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Futures Trading
What is Futures Trading in Share Market? Meaning, Types & Regulation
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Nov 3, 2025 07:56 PM IST
Summary
- Futures trading is a type of derivative trading where a contract obligates parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date.
- These contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges, ensuring transparency, liquidity, and reduced counterparty risk.
- Futures can be based on various underlying assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
- Key participantsin futures markets include:
- Hedgers: Use futures to manage price risk in the underlying asset.
- Speculators: Aim to profit from price movements without owning the actual asset.
- Arbitrageurs: Exploit price differences across markets.
- Traders must maintain a margin account, with initial and maintenance margins ensuring contract obligations are met.
- Mark-to-market: Daily settlement of gains and losses based on market prices, ensuring financial integrity.
- Futures offer leverage, increasing both potential returns and risks.
- Contract expiry, lot size, and tick size are standardized and crucial to futures trading strategies.
- Futures trading is regulated by SEBI in India, providing investor protection and market stability.
Futures trading is a type of derivatives trading where investors buy or sell contracts to purchase an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. It allows traders to speculate on the price movement of commodities, indices, currencies or stocks without owning the underlying asset. Futures trading offers opportunities for profit in both rising and falling markets but it also involves significant risk due to market volatility and leverage
What is Futures Trading in Share Market?
Futures trading meaning in the share market refers to the practice of buying or selling futures contracts which are legal agreements to trade a particular asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Unlike spot trading, futures trading allows investors to speculate on the price movement of stocks, indices or commodities without owning the actual asset. It’s widely used for both hedging and speculation offering potential for high returns but also carrying significant risk due to market volatility and leverage.
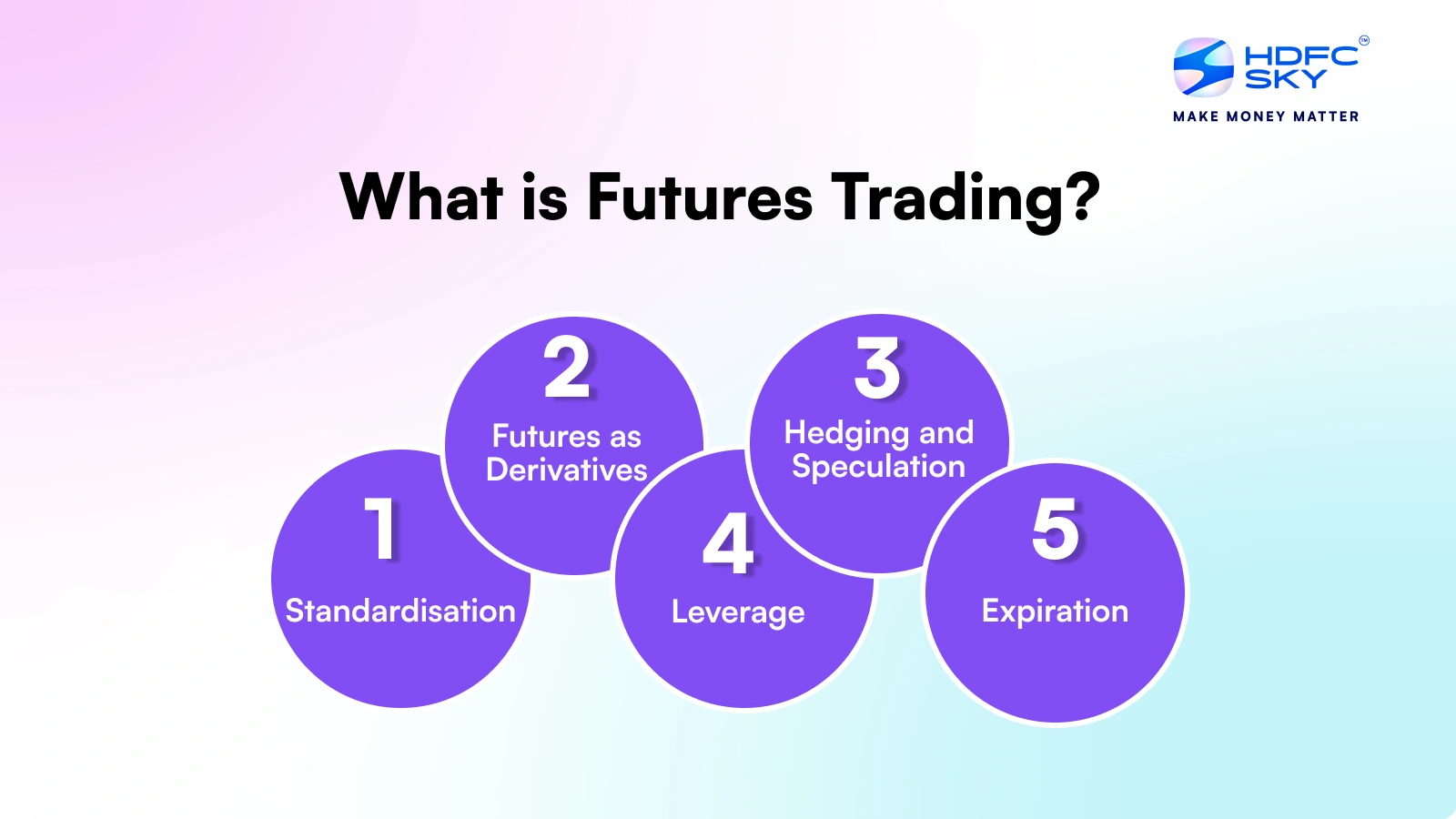
How Futures Trading is Different From Other Financial Instruments?
Futures trading stands out due to its standardised contracts, leverage, and obligation to fulfill the contract at expiry, unlike stocks or mutual funds. Here’s how it differs:
- Futures as Derivatives: Value is derived from the underlying asset (like commodities, currencies, cryptocurrencies, stocks or indices)
- Leverage: Futures require only a margin deposit, giving traders control over a larger position than their initial investment.
- Standardisation: Futures contracts are standardised in terms of quantity, quality and delivery date, making them highly liquid.
- Expiration: Unlike stocks, which can be held indefinitely futures contracts have a set expiration date.
- Hedging and Speculation: While stocks are primarily used for investments or trading, futures are widely used for hedging risks and short-term speculation.
How Future Trading Works
Futures trading works by allowing investors to enter contracts to buy or sell assets at a future date and price. It is widely used for speculation and hedging.
- Contract Agreement: Buyers and sellers agree on the asset price today for delivery on a future date.
- Standardisation: Futures contracts are standardised in terms of quantity, expiry date and settlement.
- Leverage: Traders can control large positions with a small margin amount.
- Daily Settlement: Mark-to-market adjusts gains or losses daily in your trading account.
- Expiration: On the expiry date, contracts are either settled in cash or by delivery of the asset.
How to Trade Futures in India?
Futures trading in India is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Here’s how to trade futures:
- Open a Demat and Trading Account: Choose a broker offering access to futures markets.
- Understand Margin Requirements: Depositing the initial margin is mandatory.
- Research and Analyse: Use fundamental and technical analysis to predict market movements.
- Place Orders: Buy or sell contracts through your broker’s platform.
- Monitor and Exit: Track positions regularly and close them before expiration or opt for settlement.
Examples of Futures Trading
Let’s have a look at some examples to better understand the concept of futures trading:
Speculation Example
Suppose a trader predicts crude oil prices will rise. He purchases a crude oil futures contract at ₹7000 per barrel, expiring in one month. If the price increases to ₹7500 before expiration he can sell the contract for a profit of ₹500 per barrel, minus transaction costs.
Hedging Example
Suppose a farmer in Punjab anticipates a drop in wheat prices during harvest. To hedge against this risk they sell wheat futures contracts at ₹2,500 per quintal. If the market price drops to ₹2,300 at expiration the farmer will still be able to sell at Rs 2500 per quintal. per This is an example of using futures for hedging price risk.
Types of Futures Trading
Futures markets facilitate the trading of futures contracts. They bring buyers and sellers together, providing liquidity and price discovery. Let’s explore the major types of futures:
- Financial Future: These involve assets like stock indices, government bonds, and interest rates. They’re popular among institutional investors for portfolio hedging.
- Currency Futures: Currency futures enable traders to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations or speculate on currency movements.
- Energy Futures: Crude oil, natural gas and electricity futures fall under this category. Energy companies and speculators use them extensively.
- Metal Futures: Precious metals like gold and silver along with other industrial metals like copper are traded in this category.
- Livestock Futures: These include contracts for cattle, hogs and other livestock used mainly by farmers and food processors.
- Grain Futures: Grain futures cover wheat, corn, and soybeans, helping farmers lock in prices for their crops.
- Food and Fibre Futures: Contracts for coffee, cocoa, sugar and cotton fall here. These are vital for global supply chain participants.
Difference Between Options and Futures Trading
Here is a detailed comparison between futures vs options trading:
| Feature | Futures Trading | Options Trading (From Option Buyers Perspective) |
| Nature of Obligation | Obligation to buy/sell at a set price on the expiration date. | Right (but not obligation) to buy/sell. |
| Upfront Cost | The margin requirement is low but varies. | Premium payment upfront. |
| Leverage | High leverage increases the scope of both gains and losses. | Limited leverage due to premium cost. |
| Risk | Higher potential loss. | Loss is limited to the premium paid. |
| Profit Potential | Profit potential may be higher | Profit depends on strike price and premium. |
| Market Use | Used for hedging and speculation. | Primarily for hedging and speculative trades. |
| Mark-to-Market | Daily adjustments to account values. | No daily adjustments. |
| Expiration Impact | Must close or settle the contract at expiration. | Buyer of an option can choose not to exercise the option. |
Why Should You Invest in Futures Trading?
Futures trading offers investors a dynamic way to gain exposure to various markets with flexibility and potential for high returns. Here are key reasons why investing in futures can be beneficial:
- Offers high return potential through leverage
- Allows effective risk management and hedging
- Enables speculation on price movements of diverse assets
- Provides portfolio diversification opportunities
- Helps manage and benefit from market volatility
- Allows trading in commodities, currencies, indices, and more
Advantages of Futures Trading
Futures trading offers various benefits for both investors and traders looking to hedge or profit from market movements. Here are the key advantages:
- Leverage: Trade large positions with a smaller margin, increasing profit potential.
- Liquidity: Futures markets are highly liquid, especially in commodities and indices.
- Hedging: Used to hedge against price volatility in assets like commodities, currencies, or stocks.
- Transparency: Futures are exchange-traded and regulated, ensuring fair pricing and lower counterparty risk.
- Diversification: Allows exposure to a wide range of assets commodities, indices, currencies, etc.
- Short-Selling Made Easy: Traders can easily take bearish positions without restrictions.
- Price Determination: Futures markets help in efficient price discovery due to active participation.
Disadvantages of Futures Trading
While futures trading can be profitable, it comes with notable risks. Here are the main disadvantages:
- High Risk Due to Leverage: Amplified profits also mean amplified losses.
- Complexity: Requires deep market knowledge and understanding of contract specifications.
- Margin Calls: Sudden price movements can lead to margin shortfalls, requiring additional funds.
- Time-Bound Contracts: Futures have expiration dates, limiting long-term investment options.
- Market Volatility: Prices can swing sharply, increasing the chance of significant losses.
- Emotional Pressure: The fast-paced nature can cause stress and impulsive decision-making.
Regulation of Futures
Futures trading operates under stringent regulations to ensure market integrity and protect investors. Here’s a detailed look at how futures markets are regulated:
- Regulatory Bodies: In India the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) oversees futures trading to ensure transparency, prevent fraud and maintain market stability.
Globally, organisations like the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the U.S. and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the U.K. play similar roles. - Exchange Rules: Exchanges like the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX) in India set the rules for trading futures contracts, including contract specifications and trading hours.
- Margin Requirements: Regulators mandate margins to protect against default risks. These requirements are regularly updated based on market volatility.
- Position Limits: To prevent market manipulation, regulators impose position limits, restricting the maximum number of contracts a participant can hold.
- Reporting and Surveillance: Regulators and exchanges monitor trading activities, requiring detailed reporting to detect irregularities and ensure compliance.
- Settlement Mechanisms: Rules governing the settlement of contracts, whether physical delivery or cash settlement, are strictly enforced to avoid disputes.
- Investor Protection: Measures like Investor Protection Funds (IPFs) are in place to compensate retail investors in case of broker defaults.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced new measures to regulate the derivatives market and curb speculative trading. These include increasing the minimum contract size and limiting the number of weekly option contracts.
This multi-layered regulatory framework ensures that futures trading remains fair, efficient and accessible to all participants.
Things to Keep in Mind While Trading Futures
Futures trading can be rewarding but also risky. Always trade with caution and informed decisions.
- Understand Leverage: High leverage amplifies both profits and losses.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Always protect your capital.
- Monitor Margins: Ensure you maintain the required margin to avoid forced liquidation.
- Stay Informed: Track market news and economic indicators.
- Know Contract Expiry Dates: Futures contracts have expiry; plan your trades accordingly.
- Risk Management: Never invest more than you can afford to lose.
- Start Small: Begin with smaller positions to learn the market dynamics.
- Have a Strategy: Avoid impulsive trades; stick to a clear trading plan.
Conclusion
Futures trading offers unparalleled opportunities for profit, risk management and market participation. By understanding the mechanics, markets, and applications of futures trading, traders can make informed decisions and mitigate risks. However, as with any financial instrument, futures trading requires caution and thorough preparation. To succeed in this dynamic arena, traders must stay updated on market trends, understand the underlying assets, and adopt sound practices for risk management in futures trading.
Related Articles
FAQs on What is Futures Trading
Is Futures Trading Safe?
Futures trading involves high risk due to leverage and market volatility. It’s not entirely safe and is best suited for experienced or well-informed investors.
Why Trade Futures Instead of Stocks?
Futures allow traders to leverage their investments and speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset. They also enable hedging against market volatility, making them versatile compared to stocks.
Which Is More Profitable, Futures or Options?
Profitability depends on market conditions and trader expertise. Futures may offer higher leverage, while options limit losses to the premium paid, making them suitable for different risk appetites.
What Happens If Investors Hold a Futures Contract Until Expiration?
If held until expiration, futures contracts are either physically delivered or settled in cash, depending on the contract terms.
How Can I Buy Futures?
To buy futures, open a trading account with a broker, deposit the required margin, and place an order through the trading platform.
Are Futures Traded 24 Hours?
The equity market in India is open for trading from 9:15 a.m. to 3:30 p.m. The currency derivatives market operates from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. The commodity derivatives market operates from 9 a.m. to 11:30 p.m. from March to November and from 9 a.m. to 11:55 p.m. from November to March.
How Much Funds Do I Need to Trade Futures?
The funds required depend on the initial margin requirements set by exchanges and brokers, typically ranging from 10% to 15% of the contract’s value.
Can You Day Trade Futures?
Yes, day trading in the futures market is possible. It involves buying and selling contracts within the same trading session to capitalise on intraday price movements.
How Is Futures Trading Different From Margin Trading?
Futures trading involves contracts with a specific expiration date, while margin trading involves borrowing funds to trade assets, often with no expiration.


