- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is a Demat Account?
- Importance of a Demat Account
- What is a Trading Account?
- Importance of a Trading Account
- Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
- Can You Open a Demat Account Without a Trading Account?
- How to Open Demat and Trading Accounts?
- The Buying Process of Shares
- The Selling Process of Shares
- Fees and Charges for Demat and Trading Accounts
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
- What is a Demat Account?
- Importance of a Demat Account
- What is a Trading Account?
- Importance of a Trading Account
- Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
- Can You Open a Demat Account Without a Trading Account?
- How to Open Demat and Trading Accounts?
- The Buying Process of Shares
- The Selling Process of Shares
- Fees and Charges for Demat and Trading Accounts
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
What is the Difference Between Demat and Trading Account & How to Open Demat and Trading Accounts?
By Shishta Dutta | Updated at: Oct 27, 2025 05:39 PM IST
A Demat account and a Trading account are essential tools for stock market investors but they serve different purposes. A Demat account holds your securities like shares, bonds or ETFs in electronic form, while a Trading account is used to buy and sell these securities on the stock exchange. Understanding the difference between Demat and Trading accounts helps investors manage their transactions efficiently and ensures a smooth investment journey.
What is a Demat Account?
A Demat account (short for Dematerialised account) is an account that allows investors to hold shares and securities in electronic form instead of physical certificates. It simplifies the process of trading, storing and transferring securities by eliminating the risks associated with paper-based holdings, such as loss, theft or damage. In India Demat accounts are maintained by depositories like NSDL and CDSL through registered depository participants (DPs).
Importance of a Demat Account
A Demat account is essential for holding and managing securities in electronic format, making stock market transactions safe and convenient.
- Safe Storage: Eliminates the risk of loss or damage to physical share certificates.
- Quick Settlements: Enables faster transfer of securities after a trade.
- Reduced Paperwork: Simplifies investing with minimal documentation.
- Ease of Access: Allows investors to view and manage their portfolio online.
- Cost Efficiency: Lowers transaction costs by avoiding stamp duty on transfer of securities.
What is a Trading Account?
A Trading Account is used to buy and sell securities in the stock market. It acts as a bridge between your Demat account and your bank account, allowing you to place trading orders. When you buy shares, the trading account executes the order and the shares are then credited to your Demat account. Similarly when you sell, it debits the shares and credits the proceeds to your bank account.
Importance of a Trading Account
A trading account is vital for buying and selling securities in the stock market acting as the gateway for executing trades online.
- Facilitates Transactions: Enables seamless buying and selling of stocks.
- Real-Time Access: Offers live market data and trading opportunities.
- Integrated Platform: Works alongside a Demat and bank account for smooth fund and share movement.
- Order Flexibility: Supports various order types like limit, stop-loss and intraday.
- Tracking & Analysis: Helps monitor performance and apply trading strategies effectively.
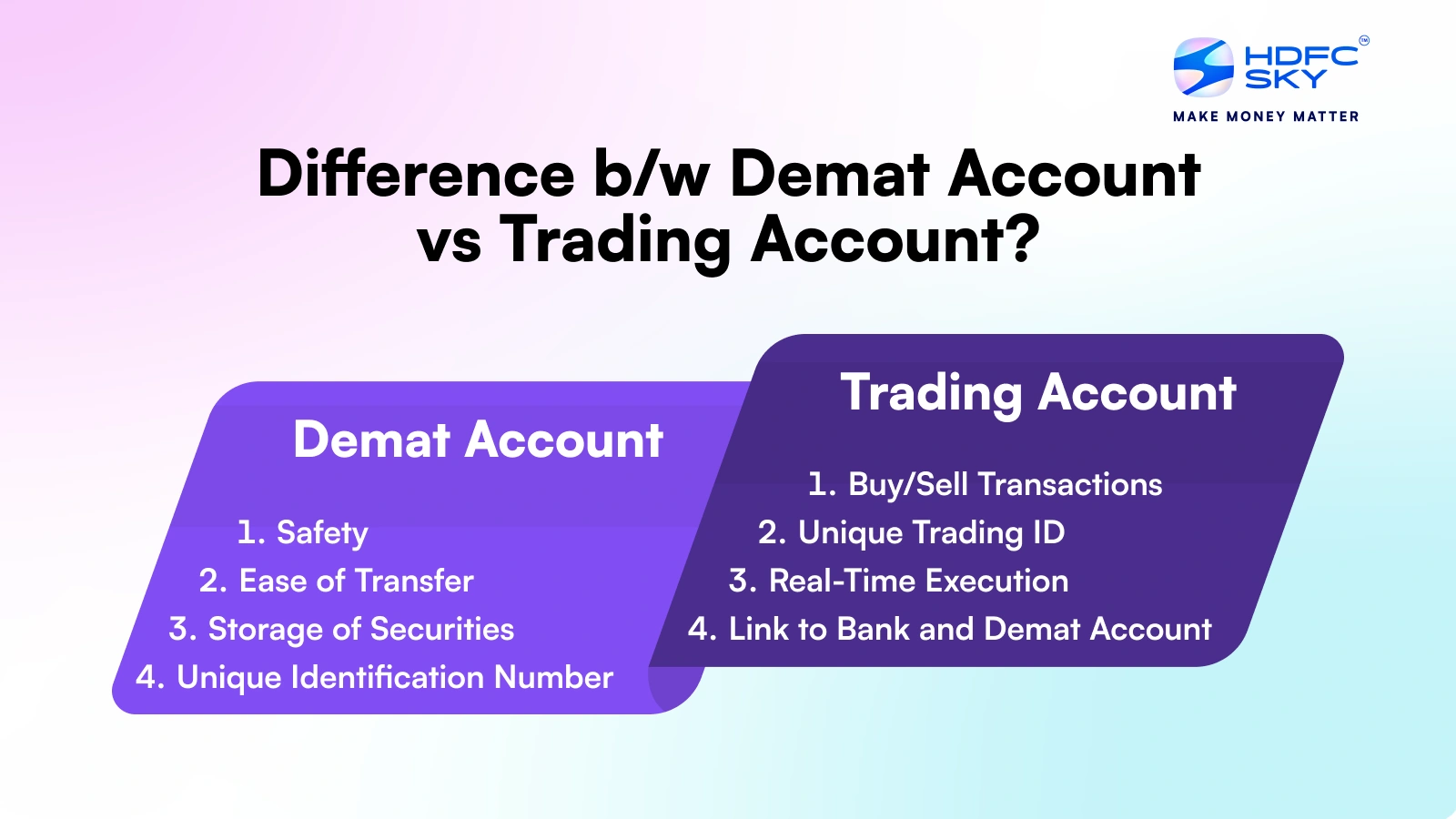
Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
In the context of trading account vs demat account, the trading account facilitates buying and selling of stocks, whereas the demat account stores them securely in electronic form.
| Particulars | Demat Account | Trading Account |
| Definition | A digital account that stores securities electronically. | An account that facilitates buying and selling of securities. |
| Role | Holds shares, bonds, ETFs and other financial instruments. | Acts as a link between your bank and Demat account to execute trades. |
| Issuing Entity | Issued by Depository Participants (DPs) registered with SEBI. | Issued by SEBI-registered stockbrokers. |
| Unique Identifier | 16-digit Demat Account Number. | Unique Trading ID or Account Number. |
| Function | Acts as a storehouse for securities. | Facilitates the placement of buy and sell orders. |
| Charges | Annual Maintenance Charges (AMC), transaction fees. | Brokerage fees per trade, no maintenance charges. |
| Link to Bank | Indirectly linked for dividend credits and fund transfers. | Directly linked to bank for funding trades. |
| Usage | For holding securities after purchase. | For buying and selling shares in the stock market. |
Can You Open a Demat Account Without a Trading Account?
You can open Demat account without a Trading account but their functionality will be limited:
1. Demat Account Without Trading Account
- A Demat account can be opened to hold securities like bonds, ETFs or mutual funds.
- However without a Trading account, you cannot buy or sell shares on the stock exchange.
2. Trading Account Without Demat Account
- A Trading account can be used for Futures and Options (F&O) and currency Trading, as these do not require a Demat account.
- However a Demat account becomes mandatory if you wish to trade in stocks.
How to Open Demat and Trading Accounts?
Demat and Trading account opening has become a quick and paperless in India. Here are the steps:
Steps to Open a Demat Account:
- Select a Depository Participant (DP) or stockbroker.
- Fill out the account opening form.
- Submit necessary documents: PAN card, Aadhaar card, bank details and address proof.
- Complete In-Person Verification (IPV) as per SEBI regulations.
- Sign the agreement and receive your Demat account number.
Steps to Open a Trading Account:
- Choose a SEBI-registered stockbroker.
- Submit the KYC documents: PAN, Aadhaar, bank proof and photograph.
- Complete verification and receive your Trading account details.
- Link your Trading account to your bank and Demat account for smooth transactions.
The Buying Process of Shares
When you buy shares, your trading and Demat accounts work together as part of a smooth and well-connected system. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how the process unfolds:
Step 1: Placing the Buy Order
Let’s say you decide to buy 50 shares of X Company at ₹1,200 per share.
You place this order through your trading account, which forwards it to the stock exchange for execution.
Step 2: Order Confirmation and Payment
Once the order is matched and confirmed:
- You need to ensure ₹60,000 (₹1,200 x 50 shares) is available in your trading account.
- This amount is usually required to be funded by the next morning (T+1 day), often before 11 AM, depending on your broker and exchange rules.
Step 3: Settlement and Share Credit
On T+2 day (two working days after the trade date):
- The purchased shares are automatically credited to your Demat account.
- No manual action is needed the process is managed by your broker and depository.
The Selling Process of Shares
When you sell shares, your trading and Demat accounts work in coordination to complete the transaction. Here is how the process unfolds:
Step 1: Verifying Share Availability
Before the sell order is processed, the trading platform checks whether your Demat account holds the required number of shares.
For example, if you are selling 300 shares of Stock X, your Demat account must reflect this quantity.
Step 2: Debiting Shares from the Demat Account
On T+1 day (one working day after the trade date), the 300 shares are debited from your Demat account and transferred to the buyer’s account.
Step 3: Crediting the Sale Amount to Your Bank Account
On T+2 day, the sale amount of ₹1,95,000 (300 shares × ₹650) is credited to your bank account via the trading account.
Fees and Charges for Demat and Trading Accounts
While opening a Demat and Trading account, some fees are applicable. Here is a comparison:
| Charges | Demat Account | Trading Account |
| Account Opening Charges | ₹0 to ₹500 (varies by broker). | Usually free or minimal. |
| Annual Maintenance Charges | ₹200 to ₹500 per year. | No AMC is generally charged. |
| Transaction Charges | Applicable for debit of shares. | Brokerage fee per transaction. |
| Dematerialisation Charges | For converting physical shares to digital. | Not applicable. |
| Brokerage | Not applicable. | Percentage or flat fee per trade. |
Conclusion
Demat accounts and Trading accounts play a crucial role in stock market investing. While a Demat account stores shares electronically. A Trading account enables buying and selling on exchanges like NSE and BSE. Together these accounts ensure smooth, secure and efficient Trading for investors.
By understanding the Trading account vs Demat account, you can better manage your investments and confidently navigate the stock market. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced investor, having both accounts is essential for participating in India’s growing financial markets.
Related Articles
FAQs on Difference Between Demat and Trading Account
Do I Need Both - a Demat Account and a Trading Account?
Can I sell shares without a Trading account?
No, you cannot sell shares without a Trading account. You need a Trading account to sell them in the market. It’s similar to having money in a savings account but needing a separate payment interface (like UPI or a debit card) to spend it.
Which Demat account is free in India?
While most brokers charge fees for Demat accounts, several new-age brokers offer zero-fee Demat accounts with no annual maintenance charges. However, it’s essential to understand that while the account might be free, other charges like transaction fees, brokerage charges, and depository participant (DP) charges may still apply.
Can I have a Trading account without a Demat account?
Yes, you can have a Trading account without a Demat account, but only if you trade exclusively in futures, options, and currencies where no physical delivery is involved. However, for Trading in stocks, having both accounts is mandatory.
Are Demat and Trading accounts the same?
No, Demat and Trading accounts serve different purposes, like how a bank locker and an ATM card serve different functions for your money. A Demat account stores your shares and securities electronically. In contrast, a Trading account is a platform through which you buy and sell these securities.
What is the difference between Demat and Trading account?
The fundamental difference in Trading and Demat accountsoften revolves around their individual functions. A Demat account is a storage facility that electronically holds your shares and securities. A Trading account, on the other hand, is your transaction platform – like an e-commerce account but for buying and selling shares.