- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is Repo Rate?
- What is Reverse Repo Rate?
- Importance of Reverse Repo Rate
- How Does the Reverse Repo Rate Work?
- Impact of Reverse Repo Rate on the Economy
- Reverse Repo Rate and Money flow
- Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- What is the Current Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate ?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Reverse Repo Rate?
- What is Repo Rate?
- What is Reverse Repo Rate?
- Importance of Reverse Repo Rate
- How Does the Reverse Repo Rate Work?
- Impact of Reverse Repo Rate on the Economy
- Reverse Repo Rate and Money flow
- Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- What is the Current Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate ?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Reverse Repo Rate?
What is Reverse Repo Rate? How Does and Impact of Reverse Repo Rate on Economy
By HDFC SKY | Updated at: Sep 22, 2025 04:06 PM IST
Reverse repo rate is the rate at which a central bank such as RBI, borrows money from banks. Most individuals take loans from financial institutions such as banks and NBFCs. The interest rates set by these institutions directly depend on the key interest rates such as the repo rate and reverse repo rate set by the Reserve Bank of India. Hence it is important to understand what is repo rate and reverse repo rate and the difference between repo rate and reverse repo rate.
What is Repo Rate?
The Repo Rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks for short-term needs by repurchasing government securities. It is a key monetary policy tool used to control inflation and maintain liquidity in the economy.
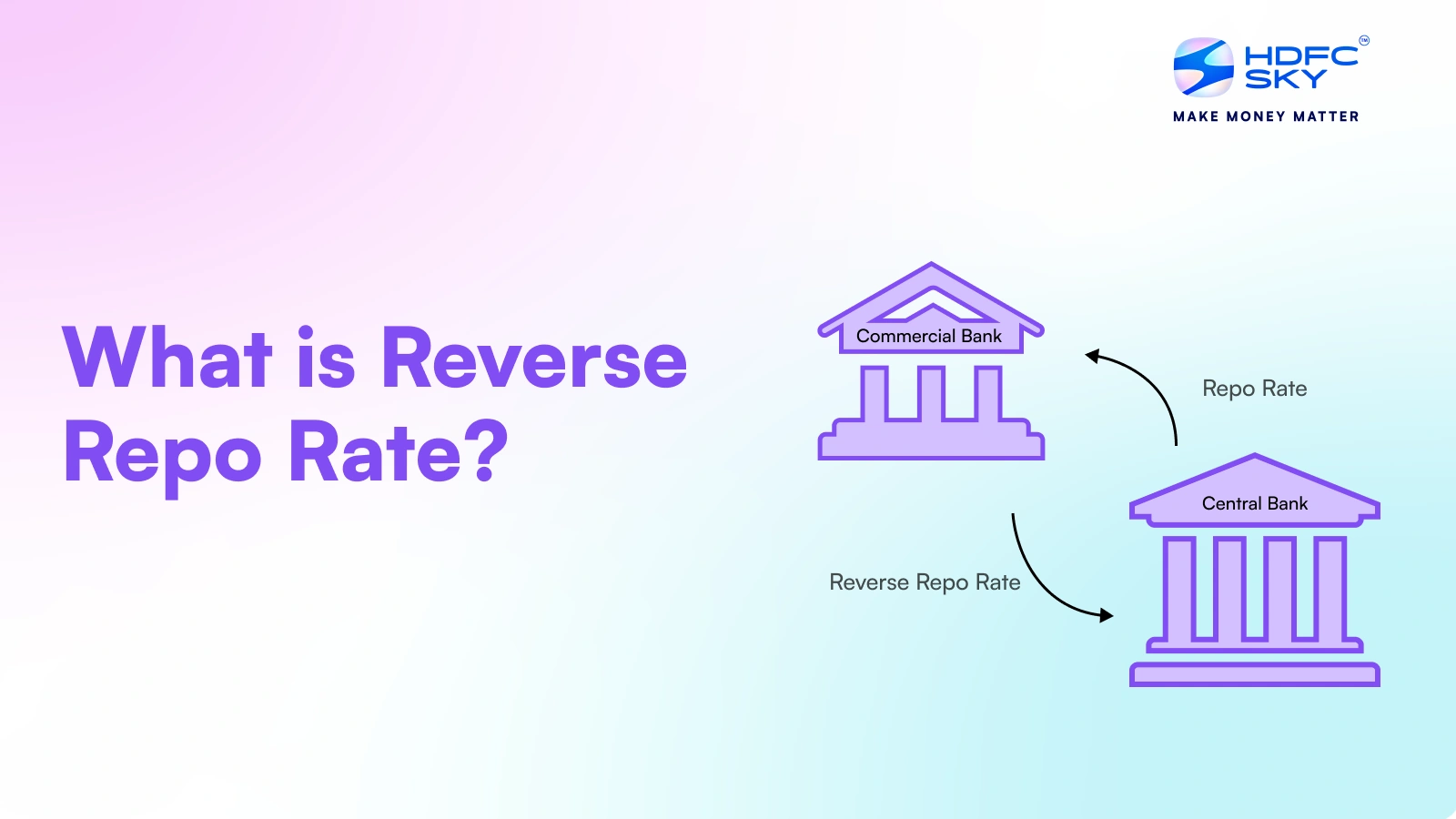
What is Reverse Repo Rate?
The reverse repo rate meaning is a rate at which the RBI takes loans from Indian commercial banks. The reverse repo rate is the opposite of the repo rate where the RBI borrows money from the banks.
In the case of reverse repo rate RBI borrows the excess money kept with the commercial banks in exchange for government securities as collateral. Similar to the repo rate, the Reserve Bank of India also sets the reverse repo rate every two to three months in its monetary policy meetings. The decision to change or keep the repo and the reverse repo rate is made by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
Importance of Reverse Repo Rate
The reverse repo rate plays a crucial role in managing liquidity and controlling inflation in the economy. It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) borrows money from commercial banks, encouraging them to park excess funds with the central bank during periods of surplus liquidity.
- Liquidity Management: Helps absorb excess liquidity from the banking system.
- Inflation Control: By reducing money supply, it indirectly helps control inflation.
- Monetary Policy Tool: It’s a critical instrument in RBI’s toolkit to maintain financial stability.
- Encourages Savings: A higher reverse repo rate can attract banks to invest with RBI rather than lend more in the market, thus tightening liquidity.
- Signal to Markets: Changes in this rate often indicate RBI’s stance on the economic outlook and monetary policy direction.
How Does the Reverse Repo Rate Work?
The Reverse Repo Rate works as a monetary policy tool used by the central bank (like the RBI) to absorb excess liquidity from the banking system. It is the rate at which commercial banks park their excess funds with the central bank for short-term periods.
When the reverse repo rate is increased, banks earn more interest by lending to the RBI so they reduce lending to the public. This controls inflation by reducing money supply.
When the rate is decreased banks get lower returns from the RBI so they prefer to lend more to businesses and consumers, thereby boosting liquidity and economic activity.
In short the reverse repo rate helps manage cash flow in the economy by influencing how much banks lend or hold.
Impact of Reverse Repo Rate on the Economy
The reverse repo rate plays a crucial role in controlling liquidity and inflation in the economy. By influencing how much banks lend or park with the RBI, it impacts overall economic growth.
1. Control of Inflation
When the RBI increases the reverse repo rate, commercial banks find it more attractive to lend money to RBI than individuals. This reduces the money supply in the economy and individuals have less money to spend. With less spending power, inflation is reduced in the economy.
2. Influence on Interest Rates
The reverse repo rate serves as a base for short-term interest rates in the economy. An increase in the reserve repo rate increases interest rates for other borrowers.
3. Bank Liquidity Management
The RBI helps manage liquidity in the banking system by adjusting the reverse repo rate. A higher reverse repo rate can absorb excess liquidity while a lower rate can encourage banks to lend more, promoting economic growth.
4. Encouragement for Investment
If RBI lowers the reverse repo rate, it makes it attractive for commercial banks to lend money to businesses and individuals rather than lending to the RBI. It encourages investments as banks have money to give out as loans.
5. Exchange Rate Effects
If the RBI changes the reverse repo rate it can affect the exchange rate. If the RBI increases the reverse repo rate, it can lead to increased foreign capital investments. As a result, the value of INR may appreciate. Conversely, the value of INR may fall if the RBI decreases the reverse repo rate as foreign investors may invest their money elsewhere.
Reverse Repo Rate and Money flow
The reverse repo rate is important in controlling money flow in the economy. It is used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to absorb excess liquidity from the banking system.
- Higher Reverse Repo Rate: Encourages banks to deposit more funds with the RBI to earn safe returns, reducing money supply in the market.
- Lower Reverse Repo Rate: Discourages banks from parking funds with the RBI, pushing them to lend more to businesses and consumers increasing money flow.
- Monetary Control Tool: RBI adjusts the reverse repo rate to manage inflation, liquidity and overall economic stability.
Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
Repo rate and reverse repo rate are monetary tools used by the RBI to manage liquidity in the economy. They serve opposite purposes in banking operations.
| Basis | Repo Rate | Reverse Repo Rate |
| Meaning | Rate at which RBI lends money to commercial banks | Rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks |
| Purpose | To inject liquidity into the banking system | To absorb excess liquidity from the system |
| Effect on Economy | Increases money supply, boosts economic activity | Decreases money supply, controls inflation |
| Interest Rate | Always higher than Reverse Repo Rate | Lower than Repo Rate |
| Usage | Used when banks face shortage of funds | Used when banks have surplus funds |
| Monetary Policy Tool | Used to combat inflation or stimulate growth | Used mainly to control inflation |
What is the Current Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate ?
As of August 06, 2025, the current reverse repo rate and repo rate are as follows:
- Repo Rate: 5.50%
- Reverse Repo Rate: 3.35%
Conclusion
The reverse repo rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from commercial banks or the rate at which the commercial banks lend money to the RBI. Repo rates and reverse repo rates are economic tools for the RBI to control the money flow in the economy. By controlling the money flow in the economy, RBI can control inflation and overall economic liquidity.
It is important to have a proper understanding of both the repo rate and reverse repo rate. Now that you know what is reverse repo rate and repo rate, you can better analyse the economic condition and make financial decisions accordingly.
Related Articles
FAQs on What is Reverse Repo Rate?
Who decides the Reverse repo rate?
The Reserve Bank of India holds its monetary policy meeting, and the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) sets the reverse repo rate.
What factors influence changes in repo rate?
The RBI analyses the current inflation rate, economic growth, liquidity, and money flow while setting the repo rate and reverse repo rate.
Is the reverse repo rate important for investors?
Yes, the reverse repo rate is important for investors as it affects liquidity in the financial system and may influence market conditions.
Why does RBI increase the reverse repo rate?
The RBI tends to increase the reverse repo rate when it is following a contractionary monetary policy. to absorb the banking system’s excess liquidity and control inflation. This move encourages banks to lend their surplus funds to the RBI rather than lending them to others, thereby managing money flow and liquidity.
How often does the RBI change the reverse repo rate?
The RBI is not required to change the repo rate. It holds monetary policy meetings every two to three months and may change or keep the reverse repo rate unchanged.
Can individuals invest in reverse repo transactions?
No, individuals cannot directly invest in reverse repo transactions, as they are conducted between the RBI and commercial banks.