- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- Calculation of the Operating Margin
- Operating Margin Formula
- Benefits of Operating Margin
- Limitations of the Operating Margin
- Operating Margin vs. Gross Margin vs. Net Margin
- What is a Good Operating Margin?
- How Is Operating Margin Different From Other Profit Margin Measures?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Operating Margin?
- Calculation of the Operating Margin
- Operating Margin Formula
- Benefits of Operating Margin
- Limitations of the Operating Margin
- Operating Margin vs. Gross Margin vs. Net Margin
- What is a Good Operating Margin?
- How Is Operating Margin Different From Other Profit Margin Measures?
- Conclusion
- FAQs on What is Operating Margin?
What is Operating Margin?
By Ankur Chandra | Updated at: Jul 28, 2025 12:56 PM IST
Summary
- Definition: Operating margin is a key profitability ratio that shows how much profit a company retains from its core operations before paying interest and taxes.
- Formula: Calculated as Operating Income ÷ Revenue × 100; it reflects operational efficiency.
- Importance: Helps investors and analysts assess a company’s ability to manage operating costs relative to revenue.
- Higher Margin Implication: Indicates better operational control and profitability; typically seen in companies with strong pricing power or cost management.
- Lower Margin Risks: Suggests vulnerability to rising costs or weak pricing strategies.
- Comparison Tool: Best used to compare companies within the same industry rather than across sectors, as margin standards vary.
- Investor Use Case: A rising operating margin trend is generally viewed as a positive signal for financial health and potential investment.

Operating profit margin (OPM) is one of the most commonly used financial ratios which displays the ability of an organization to convert net sales into operating profit. From the point of view of the investor, knowing what is OPM in the share market can give a good perspective on the stability and further development of a particular enterprise.
So in this article, we will explain what operating profit margin is, how to calculate operating profit margin, and why it is important for businesses and investors. Read along!
Calculation of the Operating Margin
Operating margin gives the percentage of profit that your business makes from the operations for each dollar rupee of sales. It is determined by using the operation earnings and it’s the percentage arrived out of total revenue.
How to Determine Operating Margin?
To calculate operating margin:
1. Determine operating profit: Subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses (like administrative costs, selling expenses, and depreciation) from total revenue.
Formula: Operating Profit = Revenue – (COGS + Operating Expenses)
2. Divide operating profit by revenue: Divide the operating profit you calculated by the total revenue to determine the operating margin.
Formula: Operating Margin = Operating Profit ÷ Revenue
Operating Margin Formula
Also, you can use the operating margin formula, which is:
Operating Margin (%) = Operating Profit ÷ Revenue × 100
For example, if your revenue is Rs. 10 lakhs, COGS is Rs. 4 lakhs and operating expenses are Rs. 2 lakhs:
- Operating Profit = 10 lakhs – 4 lakhs – 2 lakhs = 4 lakhs
- Operating Margin = (4 lakhs ÷ 10 lakhs) × 100 = 40%
This means your business keeps 40 paise from every rupee earned after covering operational costs.
Benefits of Operating Margin
Operating margin is one of the financial ratios that help you know the efficiency of your business in turning revenues into operating profit. Some more benefits of operating margin are:
- Measures Operational Efficiency: Operating margin measures the efficiency with which your firm controls its core costs such as manufacturing and selling functions. A higher level of margin reveals that cost has been well managed and resources well used within the firm.
- Provides Insight into Profitability: It shows the part of the revenue that is earned after excluding operating costs and assists you in determining the amount of gross income that is earned from operations.
- Helps Compare Performance: Operating margin is also useful when comparing your business to competitors or gauging how well your business is doing as compared to the industry’s average index.
- Tracks Financial Trends: Reporting operating margin over time allows for the identification of profitability of operation and operational efficiency. An increasing margin is good; a decreasing margin may point to an issue.
- Supports Strategic Planning: By specifying the extent to which profit has been affected by operation changes, it will be easier to decide on a new price to set, control the costs, or allocate resources.
Limitations of the Operating Margin
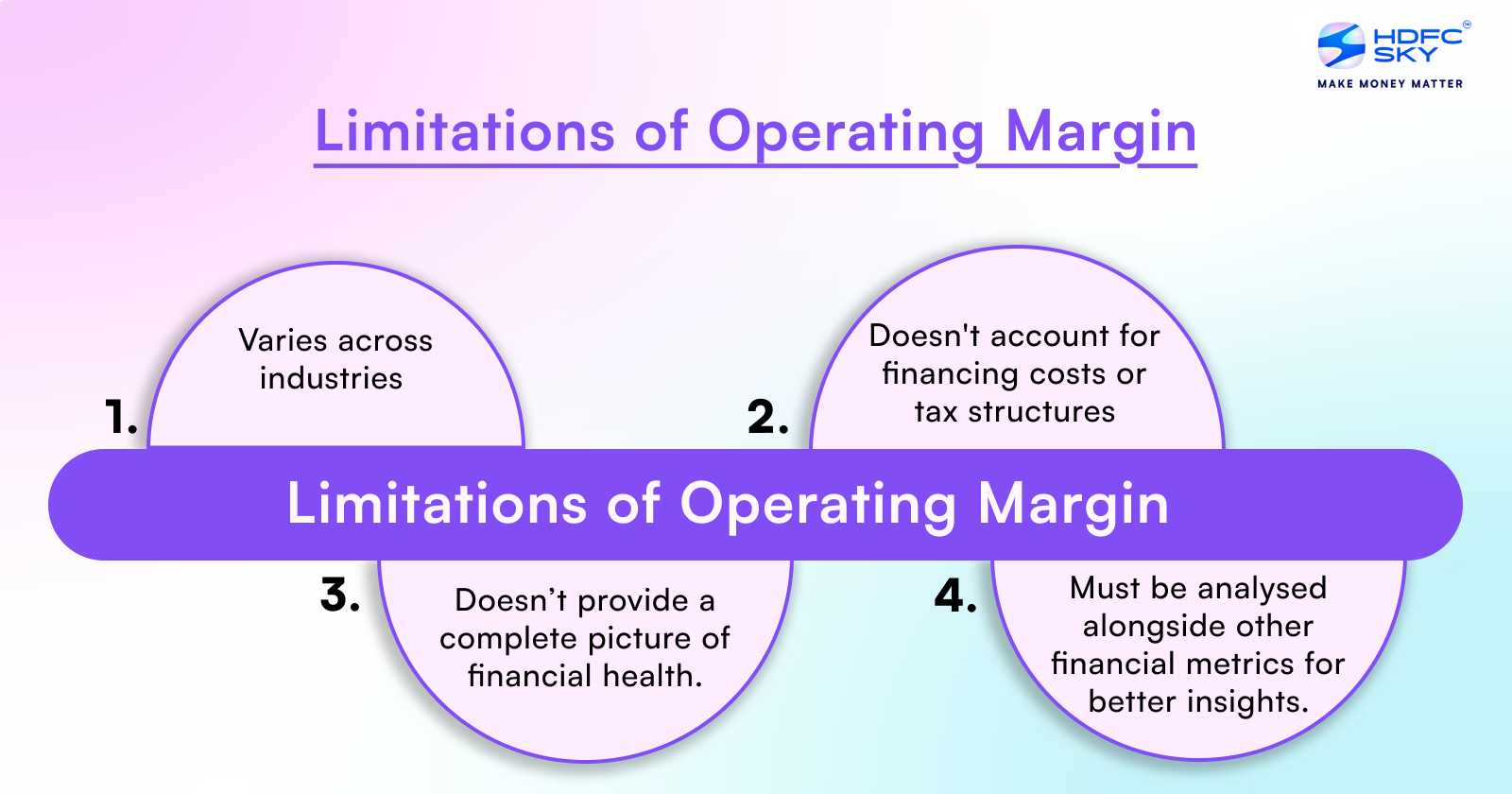
While the operating margin is a useful metric, it has its limitations, especially when comparing companies across different industries. Some of these limitations include:
- Each industry has its own business model and cost structure, which can make operating margins difficult to compare meaningfully. For example, a tech company may have a higher margin compared to a manufacturing company, simply due to the different cost structures involved.
- Operating margin doesn’t account for financing costs or taxes, which can vary significantly between companies. This makes it less useful for comparing companies with different tax structures or capital financing arrangements.
- Operating margin is influenced by how a company handles its fixed and variable costs, but it doesn’t give you a full picture of its financial health. So, it’s important to consider other financial metrics alongside the operating margin to get a clearer understanding of a company’s performance.
Operating Margin vs. Gross Margin vs. Net Margin
While all three margins—operating margin, gross margin, and net margin—provide insight into a company’s financial health, they focus on different aspects of its operations. Here’s a comparison between net margin, gross margin and operating margin:
| Margin Type | Description | Formula | Focus |
| Gross Margin | Measures the percentage of revenue remaining after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It shows how well a company can produce goods profitably. | Gross Margin = (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue | Direct costs of producing goods or services sold |
| Operating Margin | Focuses on profitability from core business operations by excluding non-operating expenses (interest, taxes). It reflects how well the company manages its operating costs. | Operating Margin = Operating Profit (EBIT) / Revenue | Core operations, including SG&A (selling, general & administrative expenses) |
| Net Margin | Represents the percentage of revenue left after all expenses, taxes, and interest have been deducted. It shows the company’s overall profitability. | Net Margin = Net Income / Revenue | Total profitability after all expenses |
What is a Good Operating Margin?
High operating margins are an indicator of how well your business can turn its core operations into profits. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all good margin but it depends on the industry you are in and the competitors that you have. Here’s a little more detail:
How Is Operating Margin Different From Other Profit Margin Measures?
The operating margin measures a company’s ability to profit from its core operations. It is calculated using the operating profit formula, which divides operating profit by revenue. However, you might come across other profit margin types, each serving a different purpose. Here’s how the operating margin compares to other key profit margins:
- Gross Margin vs Operating Margin: While the gross margin focuses only on the direct costs of producing goods or services (like materials and labour), the operating margin includes additional costs such as selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A). This makes the operating margin a more comprehensive measure of a company’s operational efficiency.
- Net Profit Margin: This metric looks at the overall profitability of the company after accounting for all expenses, including taxes, interest, and non-operating items. In contrast, the operating profit margin focuses on profits generated by core business operations, excluding those additional costs.
- EBITDA Margin: The EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) margin excludes non-cash expenses like depreciation. This provides a clearer picture of a company’s operating performance without factoring in accounting decisions or financing structures. The operating margin, however, still includes depreciation, making it a slightly more conservative measure.
Conclusion
Operating profit margin is one of the more powerful indicators that show the potential of a company to influence its operating and cost structure effectively to generate profit. As much as it is used in business analysis, understanding the operating margins is also important when checking the stocks in the share market.
Related Articles
FAQs on What is Operating Margin?
What is the operating margin meaning in simple terms?
Operating margin shows how much profit a company makes from its main operations after covering costs like salaries and materials but before paying interest or taxes. It’s calculated as a percentage of revenue. The operation profit margin formula is:
Operating Margin = (Operating Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100
How is the operating profit margin formula different from the net profit margin?
The operating profit margin formula measures profitability from core operations, excluding taxes and interest. In contrast, the net profit margin considers all expenses and income, including taxes, interest, and one-time items. Also, the operating margin focuses on operational efficiency, whereas the net margin provides a broader view of overall profitability.
What does a high operating margin indicate?
A high operating margin indicates strong operational efficiency. It shows that a company effectively controls costs and generates significant profit from its core business activities. In the share market, a high OPM suggests financial health and efficient management. However, comparisons should be made within the same industry, as benchmarks vary.
How does the operating margin ratio affect decision-making?
The operating margin ratio influences decisions by highlighting the following:
- Cost Control: Identifies if operational costs are managed effectively.
- Pricing Strategy: Indicates if revenue covers core costs adequately.
- Investment Potential: Companies with consistent operating margins are often attractive in the share market.
Is a low operating profit margin always a bad sign?
No, a low operating profit margin isn’t always negative. It might reflect:
- Investments in growth or expansion.
- Temporary cost pressures.
- Industry norms with inherently low margins (e.g., retail).