- Offerings
- Tools & Platforms
Tools & Calculators
- Open API
- Calculators
- SIP Calculator
- CAGR Calculator
- Compound Interest Calculator
- FD Calculator
- RD Calculator
- EPF Calculator
- Retirement Calculator
- HDFC SIP Calculator
- Mutual Fund Return Calculator
- Lumpsum Calculator
- Step Up SIP Calculator
- ETF SIP Calculator
- Brokerage Calculator
- Equity Margin Calculator
- SWP Calculator
- EMI Calculator
- MTF Calculator
- Pricing
- SKY Learn
- Mutual Funds
- Margin Trading
- Financial Planning
- Personal Finance
- Share Trading
- IPO
- Derivatives
- Currencies
- Intraday Trading
- Trading Strategies
- Demat Account
- Commodity
- ETF
- What is Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
- ETF Full Form
- Why Should You Consider ETFs for Your Investment Portfolio?
- Types of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- How to Invest in Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Advantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Disadvantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Risks Associated with Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Exchange Traded Fund
- What is Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
- ETF Full Form
- Why Should You Consider ETFs for Your Investment Portfolio?
- Types of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- How to Invest in Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Advantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Disadvantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Risks Associated with Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Exchange Traded Fund
What is ETF (Exchange Traded Fund)? Know ETF Full Form and Types of ETFs
By Shishta Dutta | Updated at: Jun 16, 2025 01:30 PM IST
The investment landscape is vast and often overwhelming. With the evolving dynamics of the financial markets, a common question is, “What are ETFs in the stock market?” Exchange-traded funds, commonly known as ETFs, have become increasingly popular among investors due to the diversification, transparency and wide range of assets they offer, all this with the flexibility of trading through exchanges, thereby allowing users to react quickly to movements in the market.
Understanding ETF Meaning and its structure can help investors make more informed choices. Here, we’ll delve into the features of ETFs, uncover their types and benefits, and discuss the best ways to invest in them.
What is Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
ETF Meaning refers to Exchange Traded Fund type of investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks. Unlike mutual funds which are priced at the end of the day, ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices. ETFs have become a prominent investment vehicle in the global market, offering investors a broad range of opportunities.
The objective of an ETF usually is to mimic the performance of a selected index, sector, commodity, or asset class. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios with a single purchase. Knowing what an ETF is includes recognising its ability to gain exposure to various markets, sectors, or investment strategies without having to manage multiple individual investments. Now that we’ve answered what an ETF means, let’s dive into its benefits, types, advantages, and risks.
ETF Full Form
ETF full form is Exchange-Traded Fund, ETFs hold a collection of assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or a combination of these, and are designed to track the performance of a specific index, sector, or asset class. They offer investors a diversified portfolio, cost-efficiency, and flexibility in trading, making them a popular choice for both individual and institutional investors seeking broad market exposure.
Why Should You Consider ETFs for Your Investment Portfolio?
A closer look at how ETFs can enhance your investment strategy:
- Diversification: ETFs enable investors to diversify their portfolios. For example, an ETF investment may offer you exposure to the NIFTY50 Value 20 Index, diversifying your portfolio and reducing risk.
- Cost-Efficiency: ETFs have lower expense ratios as compared to mutual funds. This makes them cost-effective – this can make a difference over the long term especially considering compounded returns.
- Transparency: ETFs usually disclose their holdings daily. This frequent transparency helps investors to make better-informed investment decisions.
Types of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
Here are the different types of ETFs:
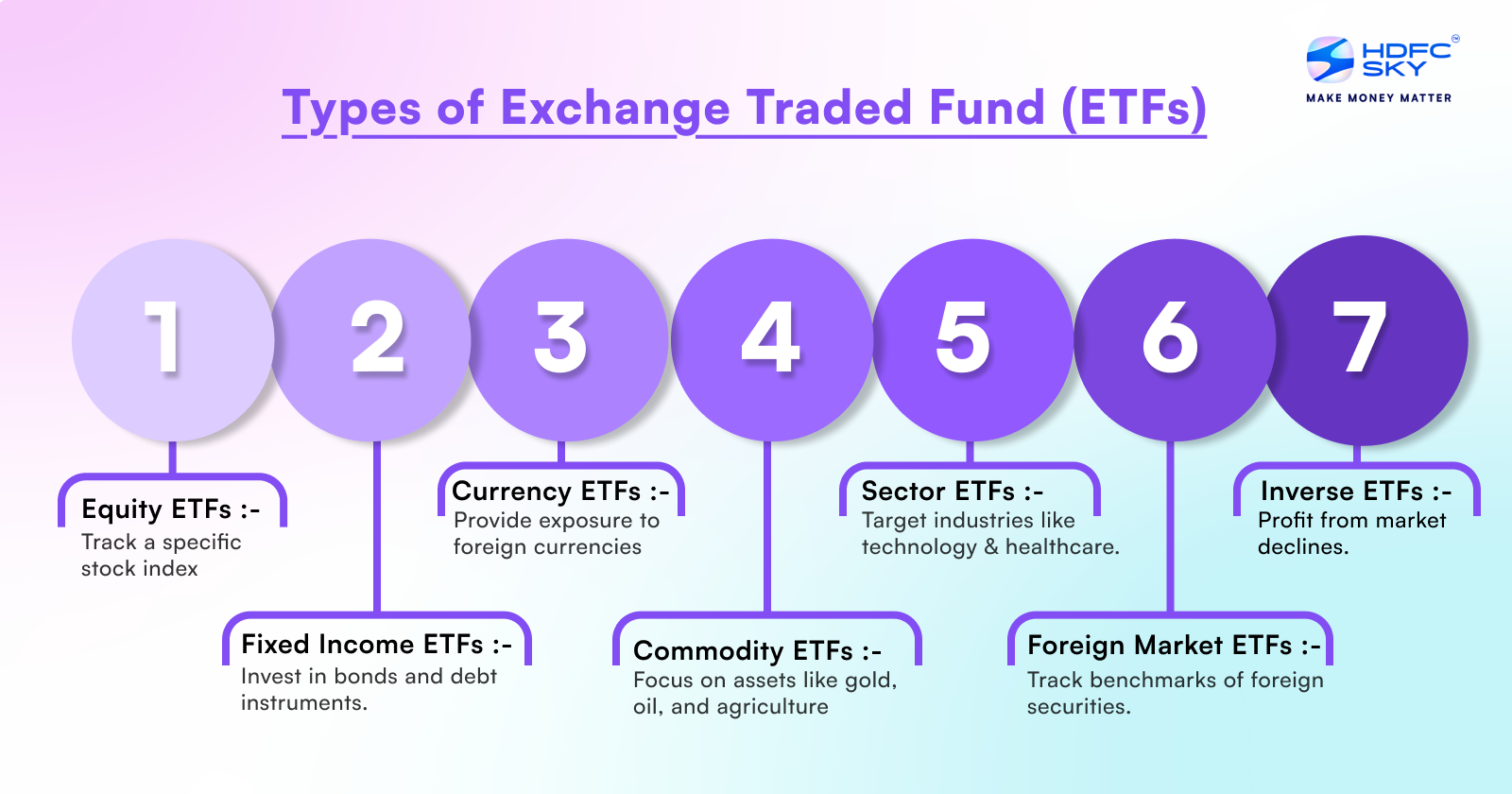
- Equity ETFs: Track a specific index of equities.
- Fixed Income ETFs: Invest in bonds and other debt instruments.
- Commodity ETFs: Dedicated to commodities such as gold, oil, agricultural commodities etc.
- Currency ETFs: Provide exposure to different currencies.
- Sector ETFs: Target specific industry sectors like technology or healthcare.
- Inverse ETFs: Designed to profit from a decline in the value of an underlying benchmark.
- Foreign Market ETF: Primarily target foreign securities. These ETF track the benchmark index of a specific country.
How to Invest in Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
Investing in ETFs is relatively straightforward but requires careful planning and consideration of your investment goals. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine Your Investment Goals: Understand your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and the amount you’re willing to invest. ETFs are available for various asset classes, so choose the ones that align with your objectives.
- Research and Select the Right ETF: When choosing an ETF, consider its expense ratio, the assets it comprises, its track record, and its liquidity. This research will help you select the most suitable ETFs for your portfolio.
- Open a Brokerage Account: You’ll need a brokerage account to buy and sell ETFs. Many brokers offer ETF investing, so it’s crucial to choose one with a platform that suits your needs.
- Place Your Order: Once you have an account, you can order an ETF. ETFs can be bought the same way as stocks, and you can purchase them at the market price or set a limit order.
- Monitor and Adjust: After investing, regularly monitor the performance of your ETFs and make adjustments to your portfolio as needed based on changes in your financial goals or market conditions.
Advantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
Our exploration of what ETFs mean in stocks reveals several advantages that make them attractive for novice and experienced investors.
- Liquidity: ETFs can be bought and sold during market hours, allowing investors to enter or exit positions as needed.
- Accessibility: A broad range of ETFs are available, allowing investors to easily access various markets, asset classes, and investment strategies, allowing for a customised portfolio.
- Transparency: Majority of ETF’s declare their holdings on a daily basis.
- Transaction type: Investors can place limit orders or stop loss orders in ETF since they are traded like stock, this gives ETF an edge over Mutual Funds.
- Portfolio Diversification: Investors can invest in different asset classes like stocks, commodities, bonds and also diversify across sectors, industries and geographic regions.
- Low Risk Investment: ETF’s help in mitigating risk by offering portfolio diversification
Disadvantages of Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
While ETFs offer numerous benefits, they are not without drawbacks:
- Trading Costs: Although the expense ratios are generally low, frequent trading of ETFs can lead to higher transaction costs, which can erode returns over time.
- Tracking Error: ETFs aim to replicate the performance of an underlying index, but due to various factors, such as fees and market conditions, discrepancies can occur between the ETF’s performance and the performance of the index it is tracking.
Risks Associated with Exchange Traded Fund (ETFs)
Investing in ETFs involves certain risks, and it’s essential to understand these risks before making investment decisions:
- Market Risk: Like any investment in the stock market, ETFs are subject to market risk. They may see fluctuations in value due to changes in the market or the performance of the assets they track.
- Liquidity Risk: Some ETFs, particularly those that focus on niche markets or less liquid assets, may face liquidity issues, making it difficult for investors to buy or sell shares at the desired price.
- Credit Risk: In the case of bond ETFs, there is a risk that the issuers of the bonds may default on their payments, leading to losses for investors.
Conclusion
ETFs have revolutionised the investment landscape by offering a versatile and cost-effective way to invest in various asset classes. Understanding an exchange-traded fund (ETF), its benefits, and the associated risks is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, ETFs can be a valuable addition to your investment portfolio, providing diversification and flexibility.
Related Articles
FAQs on Exchange Traded Fund
Can I invest in international ETFs?
Yes, you can invest in international ETFs. These ETFs provide exposure to foreign markets and can be a great way to diversify your portfolio. However, knowing the risks associated with investing in international markets, such as currency fluctuations and geopolitical events, is essential.
What fees should I be aware of when investing in ETFs?
When investing in ETFs be mindful of the expense ratio, which is the fund’s annual fee and also consider trading costs such as brokerage commissions
Are there any minimum investment requirements for ETFs?
Most ETFs do not have minimum investment requirements, making them easily accessible to investors. However, when planning your investment, you should consider the cost of individual share units and any associated trading fees.